Oral cavity Flashcards
(35 cards)



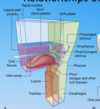
Where is the parotid duct opening?
What part of the oral cavity is this?
Upper 2nd molar.
vestibule.
What are the two compartments of the oral cavity?
Vestibule: Outside the teeth but inside the lips.
Oral cavity proper: inside the arches of the teeth.
What is the other name for the opening of the mouth?
Oral fissure.
Which ducts open into the oral cavity proper?
Submandibular and sublingual.
What two tissues will help food stay in between the teeth for mastication?
Buccinator and tongue.

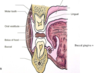

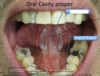
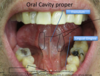
Roof, floor and exit of the oral cavity proper?

How much of the palate is hard vs soft?
Anterior 2/3 is hard. Posterior 1/3 is soft.


Which bones form the hard palate?
maxilla, palatine and sphenoid.

What are these two structures in the soft palate?


What is the purpose of palatine rugae? What happens as you travel more posterior from the rugae?
help keep the food in the mouth while it is being processed.
Travel more posterior it becomes softer and more slippery which helps it slide down
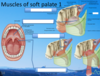

What is the palatine apenurosis?
What attaches to it and what is their function?
Palatine aponeurosis (key feature of soft palate) is tendinous fibres.
There are then muscles which attach to this aponeurosis:
Tensor palati: provide tension in the palate so the other muscels can act, this also attaches to the auditory tube which helps unblock the ears.
Levator palati: elevate soft palate.
Platopharyngeus inserts into the pharyngeas (which isnerts into the pharynx).

Palatoglossus comes from under the tongue and inserts into the palate.
Musculus uvulae inserts into the uvulae (least important.

What are in between the two arches here?

palatine tonsils

What are the two parts to the tongue? How big are they?
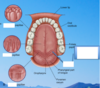
Fungiform papillae are more laterally and have taste buds.
Centrally are filiform papillae (carpet like).
Septum going down the middle.
Filiform hold the food against the teeth.

What are the intrinsic muscle layers of the tongue (from superior to inferior)?
Superior longitudinal, vertical, transverse, inferior longitidinal.
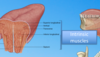
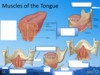

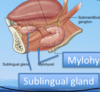
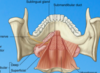
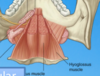
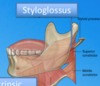
What is the muscle of the floor of the mouth?
Where does it run too and from?
Mylohyoid muscle, to and from mandible to hyoid bone.