Oral Cavity and Salivary Glands Flashcards
(84 cards)
What are the componenents of the GI Tract?
- oral cavity: teeth, tongue, salivary glands
- Pharynx
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine: duodenum, jejunum and ileum
- Large intestine: caecum, veriform, appendix, accessory colon, transverse colon, descending colon and sigmoid colon
- Rectum and anal canal
What are the main accessory organs of the digestive system?
- gall bladder
- liver
- pancreas
What is the main function of the digestive system?
preparation of food of cellulcar ultilisation
What are the 8 main processes that occur in the digestive system?
- ingestion
- masticuation
- deglutition (swallowing)
- propulsion; peristalsis and segmentation
- Mechanical digestion
- chemical digestion
- absoprtion
- defecation
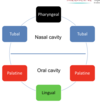
What is the oral cavity?
space between the lips and cheeks and palatoglossal folds
Alternative names for palatoglossal folds
palatoglossal arches
anterior pillars of the fauces
Where is the oral cavity proper located?
internal to the teeth
Where does the vestibule lie?
between the lips and the cheeks externally and the gums and teeth internally
What is the boundary between the oral cavity and the pharynx?
palatoglossal folds
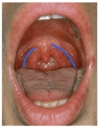
blue = palatoglossal folds
What forms the lateral wall of the oral vestibule?
cheek (buccae)
What is the cheek made up by?
- skin
- buccinator muscle
- buccopharyngeal fascia
- buccal glands
- buccal fat pad
- mucous membrane
What is the function of the buccal fact pad?
enhance the sucking capability of an infant by creating negative pressure
What is the function of the buccinator muscle?
mastication/chewing
creates continuity between the oral cavity and the pharynx
What is the buccinator muscle attached to?
maxilla, mandible and pterygomandibular raphe, where it fuses with the pharyngeal constrictor
Where do the fibres of buccinator terminate and what muscle do they contribute to?
fibres terminate in both lips and contribute to orbicularis oris muscle
What is the point of cross over of the buccinator muscle fibres called?
modiolus
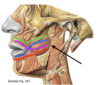
black = pyterygomandibular raphe
What constitutes the anterior wall of the oral cavity?
lips
What are the lips internally and externally lined by?
internally = oral mucosa
externally = skin
What is between the skin and the mucous membrane of the lips? Describe this zone
vermilion (red) zone of the lips
- poorly keratinised
- rich in blood vessels
What connects the lips to the adjacent gum?
median labial frenulum
Where are the small labial glands located?
between the muscle tissue and the oral mucosa and open into the oral vestibule
What forms the roof od the oral cavity and separates it from the nasal cavity?
hard and soft palate