oral pic exam 2 Flashcards
(112 cards)
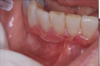
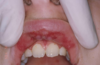
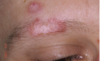
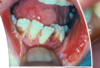
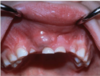
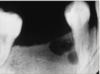
how would you describe this
desquamative gingivits
it is a clinical term, not a ds
ONLY for erosive lichen planus not reticular
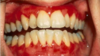
lichen planus - reticular
White striae or leukoplakia appearance
Bilateral!
Can be on other mucosal surfaces BUT buccal is the most common

lichen planus
White striae or leukoplakia appearance
Bilateral!
Can be on other mucosal surfaces BUT buccal is the most common
Commonly seen on areas that flex, like wrists, elbows etc.
They are SUPER itchy, and have a small lace like appearance to them too.

lichen planus
White striae or leukoplakia appearance
Bilateral!
Can be on other mucosal surfaces BUT buccal is the most common
Commonly seen on areas that flex, like wrists, elbows etc.
They are SUPER itchy, and have a small lace like appearance to them too.

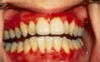
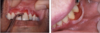
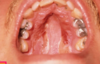
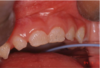
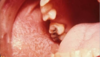
reticular lichen planus
“classic appearance”
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

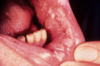
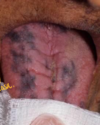
Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.
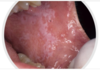
Reticular lichen planus
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.
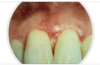
Reticular lichen planus
fine lace like apperance with some red in the background.
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.
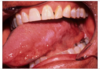
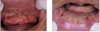
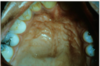
Reticular lichen planus
Here it is a plaque-like presentation of lichen planus
This is not a classic presentation.
Would still get a biopsy to confirm.
Bilateral asymptomatic white lesions of the buccal mucosa
Wickman striae lace-like appearance.
Plaque-like areas.
Normally not painful.
Can be in different surfaces like the alveolar mucosa and then onto the vestibular appearance involved.

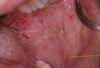
Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE

Erosive form of lichen planus
Bilateral symptomatic erythematous areas with fine white radiating striae
Central ulceration
Desquamative gingivitis → ONLY ON EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS NOT THE RETICULAR ONE
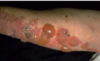
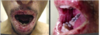
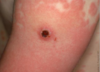
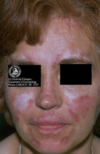
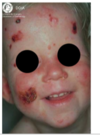
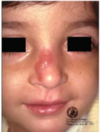
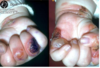
Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
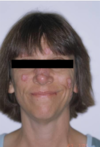
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.
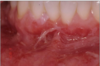
Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.

Pemphigus vulgaris
autoantibodies to desmoglein-3
Glycoprotein component of desmosomes
Tzank cells = free floating epithelial cells
Intra-epithelial split because the epithelial cells are not attached by desmosomes.
Can affect skin and mucosal surfaces
Oral lesions come FIRST then SKIN lesions
Think second = skin
Prognosis improved it tx early
May be fatal without tx.