Organisation of the brainstem and cranial nerves Flashcards
(33 cards)
What is the brainstem?
That part of the CNS, exclusive of the cerebellum, that lies between the cerebrum and the spinal cord.
What are the major divisions of the brainstem?
Medulla oblongata Pons Midbrain
What is the function of the pineal gland?
Secretes melatonin Vital for maintaining circadian rhythms- hormone release, e.g. cortisol. Day-night cycle.
Where is the pineal gland?
Dorsal midbrain, midline structure.
What is the function of the superior colliculi?
Coordinated movement of neck, head and eyes- e.g. watching tennis.
What is the function of the inferior colliculi?
Auditory reflex- turning head in reaction to loud noise.
Which cranial nerve emerges from the dorsal midbrain?
Trochlear nerve, CNIV.
What is the function of CNIV, the trochlear nerve?
Supplies superior oblique muscle of the eye.
What structure forms the roof of the 4th ventricle?
Cerebellum
Which sensory modalities are carried in the dorsal columns?
Touch and proprioception
What are the 2 dorsal columns?
Gracile fasciculus (medial) Cuneate fasciculus (lateral)
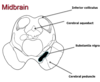
Label the following diagram:


What are the mammillary bodies?
Part of the limbic system.
Inferior part of the hypothalamus.
Where is the pituitary stalk?
Immediately behind optic chiasm, anteroinferior view of the brainstem.
Where does the oculomotor nerve (CNIII) emerge?
Midbrain.
Arises between cerebral peduncles- interpeduncular fossa.
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve (CNIII)?
Supplies majority of extrinsic eye muscles
What are the cerebral peduncles?
Surface representation of main motor tracts- corticospinal.
Structural and functional role. Fibre tract.
Hold cortex onto brainstem.
Which cranial nerve emerges from the pons?
Trigeminal nerve (CNV)
Which cranial nerves emerge from the pontomedullary junction (medial to lateral) and what are their functions?
Abducens (CNVI)- supplies lateral rectus muscle of the eye, responsible for abduction.
Facial nerve (CNVII)- supplies muscles of facial expression.
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CNVIII)- balance and hearing, innervates the inner ear in the temporal bone.
Which cranial nerves emerge from the lateral aspect of the medulla?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CNIX)- tongue and pharyngeal movements.
Vagus nerve (CNX)- main parasympathetic nerve to viscera.
Accessory nerve (CNXI)- supplies sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
What is the function of the hypoglossal nerve (CNXII)?
Supplies muscles of the tongue.
What are the pyramids?
Basis of contralateral motor control
90-95% of fibres cross over at base of medulla at the pyramidal decussation.
Continuation of corticospinal tract.
How are the spinal nerves functionally classified?
General somatic afferent (GSA)- sensation from skin and mucous membranes in the head and neck
General visceral afferent (GVA)- sensation from GI tract, heart, vessels and lungs
General somatic efferent (GSE)- muscles for eye and tongue movements
General visceral efferent (GVE)- preganglionic parasympathetic
Special somatic afferent- vision (CNII), hearing and equilibrium (CNVIII)
Special visceral afferent- smell (olfactory) and taste
Special visceral efferent- muscles involved in chewing, facial expression, swallowing, vocal sounds and turning head (CNXI)
Touch sensation from the skin on the forehead is of what functional classification?
General somatic afferent