Pain Flashcards
(34 cards)
Effect of pain on CVS + RS
CVS: tachycardia, HTN, increased O2 demand
RS: reduced VC + FRC, basal atelectasis
Describe the 3 neuron pathway of pain
1st: Site of injury - dorsal root ganglion to spinal cord
2nd: spinal cord to thalamus
3rd: thalamus to somatosensory area

Types of nociceptors + what they respond to
Mechanoreceptors = pinprick + pinch
Silent receptors = inflammation
Polymodal = pressure, heat + allogens
What are allogens?
Bradykinin, histamine, serotonin, H, K + prostaglandins
What happens when there is an injury?
Histamine + bradykinin released
Phospholipase A2 activated
Converts phospholipids to prostaglandins
Action of paracetamol
Inhibits prostaglandin production
COX 3
Action of NSAIDs
COX inhibitors
Blocks prostaglandin + thromboxane production
COX1 vs COX2 inhibitors, names + SE
1 = Ibuprofen, diclofenac
SE = bronchospasm, GI effects, renal + platelet
2 = parecoxib, celecoxib
Less SE
Action of tramadol
MU receptor agonist
Increases inhibitory descending activity (serotonin + noradrenaline)

What is the RAT system?
Recognise Assess Treat
Methods of assessing pain
Verbal rating
Visual analogue scale (VAS)
Faces pain scale (FPS)
Treatments that act on peripheral system
Non-drug: rest, ice, compression, elevation
Anti-inflammatory meds
Treatments that act on spinal cord
Non drug = acupuncture, massage
Opioids, ketamine, local anaesthetics
Drug treatments that act on brain
Paracetamol Opioids Amitryptiline Clonidine
3 layers of spinal cord
Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater

Where is the CSF?
Between pia + arachnoid aka subarachnoid space
Where does a spinal block go?
Subarachnoid space

Where does spinal cord + subarachnoid space end?
Spinal cord = L1
SA space = S1
Where does epidural space end?
Sacrococcygeal hiatus

Where can you do a spinal block?
L4/5, L3/4, L2/3
L3/4 is ideal
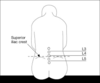
Where can you do an epidural block?
Risk of damage above L1
For labour - done at same level as spinal block
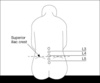
What layers does the needle pass through for an epidural + spinal?
Skin S
C fat
Supraspinous ligament
Interspinous ligament
Ligamentum flavum
EPIDURAL
Dura + arachnoid mata
SPINAL

What is a spinal block?
Single shot injection of anaesthesia into CSF
Rapid onset, anaesthesia for 2-3 hrs
Small 24G needle

What is an epidural?
LA +- opioid via catheter
Slower onset
Less motor block than spinal T
itratable analgesia for up to 72 hrs
Large 14G needle




