Palliative Care Flashcards
(37 cards)
Define palliative care
Palliative Care is an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problem associated with life-threatening illness through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial and spiritual
Define approaching the end of life
- Likely to die within the next 12 months
- Those facing imminent death and those with:
- Advanced, progressive, incurable conditions
- General frailty (likely to die in 12 months)
- At risk of dying from sudden crisis of condition
- Life threatening conditions caused by sudden catastrophic events
What are the principles of delivering foo end of life care?
- Open lines of communication
- Anticipating care needs and encouraging discussion
- Effective multidisciplinary team input
- Symptom control – physical and psychospiritual input
- Preparing for death – patient and family
- Providing support for relatives both before and after death
Describe pain experienced by those facing end of life
- Can be multifactorial
- Most patients have more than one pain
- Background/Breakthrough/Incident
Describe the physical causes of pain for those nearing the end of life
- Cancer related (85%)
- Treatment related
- Associated factors-cancer and debility
- Unrelated to cancer
What are the main types of pain syndromes?
- Bone pain
- Worse on pressure or stressing bone/weight bearing
- Nerve pain (neuropathic)
- Burning/shooting/tingling/jagging/altered sensation
- Liver pain
- Hepatomegaly/right upper quadrant tenderness
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Headache (and/or nausea) worse with lying down, often present in the morning
- Colic
- Intermittent cramping pain
Draw the WHO pain ladder
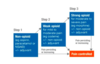
What is an adjunct medication?
other medications that have their clinical use in another area but have benefit in analgesia
What is the 1st lune strong opioid of choice?
Morphine
What are the indications for a strong opioid?
What are the main actions of strong opioids?
- Opioid receptor agonist (µ-receptors)
- Centrally acting
How are strong opioids usually administered
- Enterally – oral/rectal
- Parenterally – IM/SC injection
- Delivery via syringe driver over 24 hours
What are the principles involved in starting strong opioids?
- Principles to go by –> moving on the ‘Step 3’
- Stop any ‘Step 2’ weak opioids
- Titrate immediate release strong opioid
- Convert to modified release form
- Monitor response and side-effects
Outline modified release opioids
- Background” pain relief
- Either twice daily preparation at 12hourly intervals
- Or one daily preparation at 24hourly intervals
Outline immediate release opioids
- Breakthrough’ pain
- As required (PRN)
- E.g. Oramorph liquid/Sevredol tablets
Describe diamorphine and how it is used
- Semi-synthetic morphine derivative
- More soluble than morphine –> smaller volumes needed
- Can be used for parenteral administration (injection/syringe driver)
What is the main reason for switching opioids?
Opioid sensitive pain with intolerable side-effects
What is the main 2nd line opioid?
Oxycondone
Why are patients given oxycodone given to replace morphine?
Less hallucinations, itch, drowsiness, confusion
Why are patients prescribed a fentanyl patch?
- Second line opioid
- Lasts 72 hours
- Only use in stable pain
- Useful of oral and subcutaneous routes not available
- Useful if persistent side-effects with morphine/diamorphine
What are the most common side effects of opioids?
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Constipation
- Dry Mouth
- Biliary spasm
- Watch for signs of opioid toxicity
How is opioid induced constipation managed?
- Stimulant and softening laxative
- Senna/Bisacodyl + Docusate
- Macrogol e.g. Laxido/Movicol
- OR DO-Danthramer alone
How is opioid induced nausea managed?
- Antiemetic
- Metoclopramide
- Haloperidol (consider QT interval)
What are the main signs of opioid toxicity?
- Shadows edge of visual field
- Increasing drowsiness
- Vivid dreams/hallucinations
- Muscle twitching/myoclonus
- Confusion
- Pinpoint pupils
- Rarely, respiratory depression


