Part 1 Definitions Flashcards
(35 cards)
What is a solution? What is the solute like in the solution?
Homogenous mixture of 2 or more pure substances
In a solution, the solute is dispersed uniformly throughout the solvent. Extremely important because it helps us predict how the solution behaves and allows us to perform calculatio
What is the solute definition vs solvent definition?
What is solubility?
solute - substance being dissolved
solvent - present in greater amount
Solubility - amount of a substance that dissolves in a given amount of solvent (usually H20)
What are some common types of solutions?
Air in gaseous solution == solute gas == solvent gas
club soda == solute gas == solvent liquid
vodka == solute liquid == solvent liquid
seawater == solid solute == solvent liquid
brass == solute solid == solvent solid
3 types of homogenous mixture and their consequences
1. solids in liquids (hydration vs solvation)
Solvation, is the process of attraction and association of molecules of a solvent with molecules or ions of a solute.
Hydration is the process of attraction and association of molecules of water with molecules or ions of a solute
2. liquids in liquids (miscible vs immiscible)
Miscible substances fully mix in all proportions
Immiscible substances never fully mix in any proportions
3. gases in liquids (Henry’s Law)
(concentration of dissolved gas ) = (partial pressure of gas) x (solubility coefficient)
What is hydration and solvation?
What is Henrys Law?

What is miscible vs immiscible?
What is unsaturated and saturated and supersaturated?
Unsaturated: contains less than the maximum amount of solute
Saturated: contains the maximum amount of solute

What is equilibrium saturation?● Equilibrium: dissolution and crystallization occur at opposite rates
Equilibrium: dissolution and crystallization occur at opposite rates
What determines solubility?
Entropy (tendency towards mixing from disorder)
Intermolecular Forces
Affect but do not determine: Temperature and Pressure
How does entropy determine solubility?
A thermodynamic quantity representing the unavailability of a system’s thermal energy for conversion into mechanical work, often interpreted as the degree of disorder or randomness in the system.
DISORDER
How do IMFs determine solubility?
The intermolecular forces between solute and solvent particles must be strong enough to compete with those between solute particles and those between solvent particles.
How do solutions form?
As a solution forms, the solvent pulls solute particles apart and surrounds, or solvates, them.
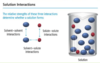
What are the relative interactions that determine if a solution forms?

Describe salt in solution?
If an ionic salt is soluble in water, it is because the ion- dipole interactions are strong enough to overcome the lattice energy of the salt crystal.
What are the 3 steps that affect the energetics of solution?
3 steps that affect the energetics of solution:
- Separation of solute particles,
- Separation of solvent particles,
- New interactions between solute and solvent.

What is Hess’s Law?

What is Hess’s Law the sum of?
Hess Law: the overall enthalpy change in solution formation, called the enthalpy of solution (ΔHsoln) is the sum of the changes in enthalpy for each step:
deltHsoln = deltaHsolute + deltaHsolvent + deltaHmix
Reminder: Enthalpy (H) is the sum of the internal energy (U) and the product of pressure and volume (PV). Has units of kJ/mol.
H = E + PV
What parts of Hess’s Law (deltaHsoln) are positive or negative (endothermic or exothermic) and why?
deltaHsolute
endothermic (+) AND always > 0
requires energy to break interactions in solute
deltaHsolvent
endothermic (+) AND always > 0
requires energy to break interactions in solvent
deltaHmix
exothermic (-) AND always < 0
releases energy to form new interactions (solute + solvent)
What are the 2 possible outcomes of heat?
exothermic releases heat against increasing energy
endothermic absorbs heat against increasing energy

What is the third reaction of a solution from Hess’s Law?

What happens to the Hess Law equation for deltaHsoln to be equal to about 0?
if the sum of the endothermic terms is approximately equal in magnitude to the exothermic term, then deltaHsoln is about zero
deltHsolute + deltHsolvent ~ deltaHmix
Why do endothermic processes occur?
Because of entropy!
Do both endothermic and exothermic process occur at the same time in solution?
Yes, both of these are spontaneous because of entropy