Part 1: Nervous System and Spinal Nerves Flashcards
(43 cards)
Central Nervous System composition and role:
- comprised of neuronal cell bodies, nerve fibers, and connective tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
- regulates and coordinates body functions
Collections of neuronal cell bodies within the CNS are called:
nuclei
The nerve fibers of the CNS are commonly arranged into discrete bundles called:
tracts
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) composition and role:
- Comprised of the neuronal cell bodies, nerve fibers and connective tissues that lie outside the CNS.
- Convey information between the CNS and peripheral structures.
Collections of neuronal cell bodies outside the CNS (in the PNS) are called:
ganglia
Somatic PNS composition and role:
- Comprised of peripheral nervous tissue responsible for carrying signals to and from skeletal muscles, tendons, joints and skin.
- Conveys general sensations of pain, temperature, touch and proprioception from the periphery to the CNS.
The cell bodies of lower somatic motor neurons are located in:
the ventral horn of the spinal cord
The cell bodies of somatic sensory neurons are located in:
dorsal root (spinal) and cranial nerve ganglia.
Viscera refers to:
the internal organs of the body
Autonomic PNS composition and role:
- Comprised of peripheral nervous tissue responsible for carrying signals to and from the viscera.
- Conveys viscera sensations such as distension.
- Sympathetic and parasympathetic components.
The two components of the Autonomic PNS:
- sympathetic component; “fight or flight”
- parasympathetic component; “rest and digest”
- Both utilize two motor neurons in the peripheral path to innervate smooth and cardiac muscle.
Role of parasympathetic component of autonomic PNS:
- controls digestive functions, slows the heart rate and constricts the pupils.
Role of sympathetic component of autonomic PNS:
- controls pupillary dilation, increased heart rate, blood pressure and sweating.
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic components of the autonomic ANS innervate smooth and cardiac muscle?
two motor neurons in the peripheral path.
Neuron structure:
cell body, dendrite(s) and an axon.
Neurons can be classified as:
- multipolar, bipolar or unipolar based upon the number of processes associated with their cell body.
- motor (efferent) or sensory (afferent).
Motor (efferent) Neurons:
- multipolar and carry information away from the CNS.
- cell bodies located in nuclei within the ventral horn of the spinal cord.

Cell bodies of somatic motor neurons are located in:
- nuclei within the ventral horn of the spinal cord.
Somatic motor neurons stimulate:
- contraction of skeletal muscle.
- nuclei are in ventral horn.
Sensory (afferent) Neurons:
- unipolar and carry information towards the CNS.
- cell bodies clustered in ganglia located outside the CNS.

Cell bodies of somatic sensory neurons are located in:
ganglia located outside the CNS
Ganglia associated with spinal nerves are called:
dorsal root ganglia (spinal ganglia).
The spinal cord lies within the vertebral canal extending from:
- the foramen magnum to the level of the intervertebral disc between L1/L2 vertebra.
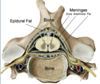
The spinal cord is surrounded by:
- bone
- epidural fat
- three meningeal layers:
- dura mater (outermost),
- arachnoid mater (intermediate)
- pia mater (innermost)
- cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that fills the subarachnoid space.