PATHO - Reproductive System Flashcards
(174 cards)
Female gametes are known as ____________.
Male gemetes are known as __________.
Each gamete contains _____ chromosomes. Female x male gametes unite together to form a ____ chromosome zygote.
Female gamete: ovum
Male gamete: spermatozoon (sperm cell)
Each gamete: 23 chromosomes
Joins together to form a 46 chromosome zygote
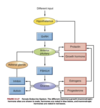
Classification of sex hormones
steroid hormones
all made from cholesterol
Function of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in females and males
- from adrenal gland, ovary, other tissues
- Females & Males : converted to androstenedione ⇒ estrogens, testosterone, both
Function of estrogens in females and males
- estrone, estradiol, estriol - works on estrogen receptors 𝝰 & 𝛃 (in ovary and placenta, small amounts in other tissues)
-
Females: stimulates development of female sex traits:
- breast, uterus, and vaginal maturation
- proliferation of endometrium during menstrual cycle
- mammary gland development during pregnancy
- promotes fetal adrenal gland function
- uteroplacental blood flow
- Males: growth at puberty, fusion of bone growht plate, preventing apoptosis of germ cells
Source and function of testosterone in females and males
- Source: adrenal glands (from DHEA), ovaries
- Females: libido, learning, sleep, protein anabolism, growth of muscle and bone, pubic and axillary hair, activation of sebaceous glands, contributes to acne
- Males: stimulates spermatogenesis, development of 1’ and 2’ sex tracts, bone and muscle growth, pubic and axillary hair, activates sebaceous glands, contributes to acne, maintains libido
Source and function of GnrH in females and males
- Source: neuroendocrine cells in hypothalamus
- Females & males: stimulates secretion of gonadotropins (FSH an dLH) from anterior pituitary
Source and function of FSH in females and males
- Source: gonadotroph cells from anterior pituitary
- Females: promotes development of ovarian follicles, stimulates estrogen secretion
- Males: promotes development of testes, stimulates spermatogenesis by Sertoli cells
Source and function of LH in females and males
- Source: gonadotroph cells in anterior pituitary
- Females: triggers ovulation; rpomotes development of corpus luteum
- Males: stimulates testosterone production by Leydig cells of testes
Source and Function of Inhibin in females and males
- Source: ovary and testes
-
Females & Males: inhibits FSH production in anterior pituitary
- in females, Inhibin B is primarily secreted in follicular phase but spikes when ovulation occurs
- Inhibin A is secreted during luteal phase and further supresses FSH
- also restrains prolactin and GH release, inteferes with GnRH receptors, and promotes breakdown of itnracellular gonadotropins
- activity boosted by follistatin
Source and Function of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) in females
- Source: placenta
- Females: supports corpus luteum, which secretes estrogen and progesterone during first 7 weeks of pregnancy
Source and function of Activin in females
- Source: ovary (granulosa cells)
- Females: stimulates secretion of FSH and pituitary response to GnRH and FSH binding in dominant granulosa cells
- inhibited by follistatin
Source and Function of progesterone in females
- Source: ovary and placenta
- Females:
- promotes secretory changes in endometrium during luteal phase of menstrual cycle
- quiets uterine muscle activity
- prevents lactogenesis during pregnancy
Source and function of relaxin
Source: corpus luteum, myometrium (uterine muscle), placenta
Function: inhibits uterine contractions during pregnancy and soften pelvic joints and cervix to facilitate childbirth
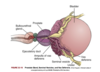
In early embryonic development, the reproductive structures of male and female embryos are ____________.
They consist of a pair of primary sex organs known as ________ and two pairs of ducts which are _____________ and _____________.
In early embryonic development, the reproductive structures of male and female embryos are homologous (the same)/undifferentiated.
They consist of a pair of primary sex organs known as gonads and two pairs of ducts which are mesonephric (wolffian) and paramesonephric (müllerian) ducts.
What are the mullerian ducts?
How may these ducts change in females vs males?
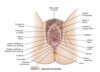
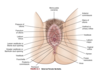
- precursors of the internal female sex organs (oviducts, uterus, cervix, upper vagina)
- initially formed regardles sof genotypic sex (no SRY signaling needed for development)
- SRY signaling is needed in males for these ducts to regress and prevents deelopment of female reproductive tract
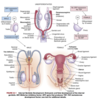
What are wolffian ducts? What is their function?
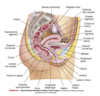
precursor of male internal sex organs
secretes testosterone and promotes development of male sex organs

The first sign of development of reproductive organs (male/female) occurs during _____ week of gestation.
5th
What kind of effect does the SRY gene have on embryonic differentiation?
- sex-determining region of the Y chromosome
Where is Muwllerian inhibitory hormone (MIF) secreted from?
What is the function of Muwllerian inhibitory hormone (MIF) in reproductive development?
Source: secreted by Sertoli cells in the testes
Function: promotes degeneration of the müllerian ducts
- No MIF, the müllerian ducts would develop and wolffian ducts would degenerate with loss of male sex organ development
At what age would the male gonads (testes) descend into the scotum?
At what age would the testes produce sperm?
Descend into the scrotum: 9 months
Sperm production: after puberty
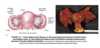
How does female gonadal development occur?
- development occurs due to absence of SRY expression
- estrogen is present while testosterone and MIF are absent which lead to loss of wolffian system; also promotes development of external genitalia
- 6-8 weeks’ gestation: two female gonads develop into ovaries
- mesonephric ducts deteriorate and upper ends of paramesonephric ducts decome fallopian tubes
Where do external reproductive structures stem from and how do they develop from these precursor structures?
Source: homologous embyronic tissues (i.e. undifferentiated)
Development: at 7-8 weeks gestation, the male & female embryos develop genital tubercle (elevated structure). The tubercle relies on testosterone for differentiation into external male genitalia or else female genitalia will develop in the absence of ovaries

Describe when and what occurs during development of the endocrine system in utero that contributes to sexual differentiation.
4/5 weeks gestation: anterior pituitary development begins
10 weeks: GnRH produced in hypothalamus - contraols production of LH and FSH in anterior pituitary
12 weeks: vascular connection between hypothalamus and pituitary is established
28 weeks: in female fetus, high levels of FSH and LH are excreted (up until 28 weeks) and stimulate production of estrogen and progesterone by the ovary. At ~28 weeks, etrogen and progesterone levels in ovaries and placenta are high enough so gonadotropin production decreases
Females:
Production of ova occurs (during fetal life/at puberty).
How many female gametes mature per menstrual cycle?
Males:
Production of sperm occurs (during fetal life/at puberty).
How many sperm are produced daily?
Females:
ova production occurs during fetal life
one female gamete matures per menstrual cycle
Males:
sperm production occurs at puberty
Millions are produced daily, for life