Pediatric genetics Flashcards
(63 cards)
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (“brittle bone disease”) is autosomal <u> </u> and involves what genes
- autosomal dominant
- genes alpha-1 and alpha -2 chains of type I collagen (COLA1 or COLA2)
list the types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- Type I: Mild
- Type II: most severe (prenatal lethal)
- Type III-IX: moderate to severe
Blue sclerae is indicative of
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
clinical presentation
- short stature
- limb deformity
- scoliosis/kyphosis
- basilar skull deformity
- blue sclerae
- hearing loss
- opalescent teeth
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
What imaging findings are consistent with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- Wormian bones (suture bones)
- codfish vertebrae (compression fx)
what labs should be done to evalulate for Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- biochemical testing: evaluate structure and quality of type I collagen
- labs: vit D, phosphorous, alk phosp may be elevated
treatment of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- Bisphosphonates-Pamidronate
- slows down bone resorption
- reduces fx rates and increases bone density
adverse effects of Bisphosphonates-Pamidronate
- hypocalcemia
- osteonecrosis of jaw
- nephrotoxicity
Marfan syndrome is autosomal . What gene is affected
- autosomal dominant
- FBN1 (fibrillin)
What cardiac abnormalities are associated with Marfan’s syndrome
- aortic dissection
- mitral valve prolapse
What pulmonary abnormalities are associated with Marfan’s syndrome
predisposed to spontaneous pneumothorax
What ophthalmologic abnormalities are associated with Marfan’s syndrome
- myopia
- lens subluxation/dislocation
clinical presentation
- tall, thin
- increased arm span/height ratio
- scoliosis
- arachnodactyly
- pectus deformity
- hindfoot valgus
- hypermobile joints with laxity
Marfan’s syndrome
The steinberg sign
(A): positive if thumb tip extends from palm of hand
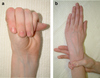
The walker-Murdoch sign
(B) positive if thumb and fifth finger overlap

How is Marfan’s syndrome diagnosed
- CVS or amniocentesis
- DNA testing
Prader-Willi Syndrome is caused by
- spontaneous
- long arm of chromosome 15
- absence of paternal gene expression
Prader-Willi Syndrome leads to dysfunction of
hypothalamus or pituitary
what is genetic imprinting
expression of gene depends on gender of parent donating this gene
loss of maternal copy of chromosome 15 results in
angelman syndrome
Prader-Willi Syndrome can be due to either
- paternal deletion: 75% of cases
- maternal disomy
- two copies of chromosome 15 inherited from mother
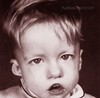
clinical presentation
- narrow forehead
- triangular mouth
- short
- depigmentation: skin and eyes
- hypogonadism
- intellectual delay
- food seeking behavior
Prader-Willi Syndrome
This is characteristic of Prader-Willi Syndrome and is seen in infants and then changes in early childhood
- infants: profound hypotonia
- feeding difficulties
- early childhood: Hyperphagia and weight gain
- binge eating
How is Prader-Willi Syndrome diagnosed
- molecular genetic test
- methylation analysis