Pediatric Infectious Diseases Flashcards
(27 cards)
8 questions to ask if infection suspected
- how sick?
- do I need to start tx immediately
- how old?
- infections sneaky and DEADLY in neonates
- immunizations up to date?
- what season is it, any outbreaks?
- history of current illness
- what, when, how much, how bad?
- medical history
- recurrent infections, similar sx, recent tx, surgeries, meds (immunosuppressive drugs), shunt, catheter
- exposures
- home, daycare/school, travel, animal, ticks, mosquitoes, soil contamination, chemicals
- sanitation
- water, food sources, cleanliness
Review Text Table 93-2
overview of where infections may be overlooked
Actions for Fever in Infants < 3mo
- ask the questions
- determine site of infection
- determine course of treatment
* look for serious infetions 1st!
- sepsis, UTI, meningitis, herpes
- perform lab tests as indicated
- MC: Group B strep, E coli, Listeria, Strep pneumo, H flu, Salmonella, Neisseria, Staph aureus
Actions for Fever in Children 3mo - 3y
- ask the questions
- do you have time to assess or is immediate tx required
- EXPECT viral infections - self limited
- labs not usually indicated (but may be key to some)
- look for zebras!
Labs for Fevers
- rapid strep
- monospot/EBV titers
- CBCd
- ESR, CRP
- procalcitonin, presepsin (check for sepsis)
- UA
- cultures: blood, urine, CSF, wound, mucous, membrane, rectal swab, stool
- metabolics: electrolytes, LFT’s, amylase, lipase
Evaluation of Prolonged Fever
- repeated cultures
- serology: CMV, HIV, toxoplasmosis, etc.
- abdominal US
- CT: chest, abdomen, etc.
- MRI if indicated
- endoscopy
- radionuclide: occult abscess, bone scan
Course for Fever >2 weeks w/ unknown cause
refer to infectious disease
http://reference.medscape.com/features/slideshow/fever-unknown-origin#page=1
hematogenous infection key points
sepsis
- presents as ill child w/ rapid progression
- treat first - culture as you go
- get causative organism and sensitivities
- monitor closely for deterioration
- measure clotting factors
- renal/liver function
- electrolyte levels
common worldwide/all year infection w/ wide presentation
(polio vs. non-polio)
some non-polio can infect spinal tract causing paralysis/death
enteroviruses
vesicles on tonsillary pillars and sore blisters on hands/feet
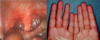
Coxsackievirus
(hand foot mouth disease)
- may cause non-specific febrile illness, aseptic meningitis, encephalitis, hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, non-specific viral rashes
- though to be the underlying illness that leads to Type I DM
“slapped cheek” appearance / “drawn on” rash

Erythema infectiosum
(Fifth disease - Parvovirus B19)
- very mild, often asymptomatic until rash presents
- no contageous when rash presents
- SPONTANEOUS ABORTION if contracted in 1st 1/2 of preg.
- serious disease, chronic anemia in immunocompromised
Herpesviruses
(8 type infect humans)
become dormant for a lifetime
- chickenpox
- cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- herpes simplex (HSV)
- genital herpes
- infectious mononucleosis (EBV)
- Roseola
rash up back of neck and along hairline, good disposition

Roseola infantum - Herpesvirus 6
(exanthema subitum, pseudorubella)
- high fever (103-105) for 3-5 days
- no symptoms other than fever, malaise MC
- fever plummets around day 4 then rash develops
fever, pharyngitis, fatigue, lymphadenitis
(biggest concern if congenital infection!)
Cytomegalovirus
- rapid progression causing liver and spleen enlargement
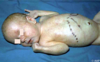
oral lesion (fever blister) w/ typical viral symptms:
fever, irritability, poor oral intake, oral lesions, herpetic whitlow
(congenital often deadly! - look for scalp vesicles)

Herpes simplex Type 1
(NOT and STD)
fever, malaise, genital vesicles
can be primary infection or tansmitted in birth canal
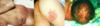
Herpes simplex Type 2
- C-section can reduce but not prevent exposure
- Ill newborns treated w/ variety of antibacterials AND antivirals pending diagnosis
- early antiviral my prevent encephalitis
pharyngitis “hot potato voice” and lymphadenitis
fever, fatigue, malaise
+/- splenomegaly

Infectious Mononucleosis - EBV
- must be diagnosed w/ labs
- Monospot
- EBV titers
-
exclusion from contact sports for 6 weeks
- IgM / herterophile 1st
- IgG
- EA
red, bulging eardrum; opaque appearance w/ fluid behind TM

Acute Otitis Media
- Tx:
- Amoxicillin
- Omniceph (cephalosporins) if Amoxicillin failure
- Ceftiaxone IM x3 if severe/persistent or oral not tolerated
- Azithromycin (Zithromax) if PCN allergy
- NOT ideal for upper respiratory pathogens
- Antibody drops first line if tubes in place
mucopurulent eye discharge w/ redness, high % AOM, no itching
Bacterial Conjunctivitis (MC than viral)
- MC: H flu, Strep pneumo, S pyogenes
- vaginal flora in neonates: Klebsiella, E coli, Staph epi
- complications:
- periorbital cellulitis
- meningitis
- Tx
- polymyxin/trimethoprim (Polytrim) - cheap
- fluoroquinilone drops - better coverage, more expensive
watery eyes w/ redeness and low incidence of AOM, no itching
Viral Conjunctivitis
watery eyes w/ redness and no AOM, severe itching
Allergic Conjuntivitis
conjunctivitis d/t immune complex vasculitis
Kawasaki disease
- non-infectious
- presents w/ other symptoms of Kawasaki disease
conjunctivitis d/t immune mediated hypersensitivity affecting mucous membranes - typically drug reaction
(what is pathognomic and treatment)
- prodrome fever, cough, HA, malaise
Steven Johnson syndrome
- pathognomic:
- target lesion rash with vesicular, purpuric, or nectrotic center
- tx:
- withdraw offending agent (antibiotic) and supportive care


