Pediatrics Flashcards
(22 cards)
What causes Caput Seccedaneum? Does it cross the suture lines?
caused by pressure of the fetal head against the cervix during labor, which decreases blood flow to the area resulting in edema
Yes, it crosses the suture lines
What causes Cephalohematoma? Does it cross the suture lines?
Subperiosteal hemorrhage that is usually caused by delivery assistance devices
No, it does not cross the suture lines
A large for gestational age baby is born via spontaneous vaginal delivery. You perform the post-birth physical exam and notice crepitus and discontinuity on the left clavical. What is your diagnosis? What is the treatment?
Clavicular fracture
No treatment needed as a callus will form in roughly a week
A large for gestational age baby is born via spontaneous vaginal delivery. You assess the Moro exam and notice the right arm remains extended and medially rotated. What is the diagnosis and treatment?
Erb-Duchenne’s palsy (waiter’s palsy) C5-6
Typically resolves on its own but if not better by 3-6 months, refer for neuroplasty
Diagnosis? Does it go away? If you biopsy it, what will you see?

Slate Gray Nevus
Typically goes away during adolescence
Biopsy: melanocytes
Diagnosis? Does it go away?

Nevus simplex
Usually goes away
Diagnosis? Does it go away? If you biopsy it, what will you see?

Milia
Usually goes away
Biopsy: Keratin
Diagnosis? Does it go away? If you biopsy it, what will you see?
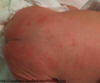
Erythema toxicum (it’s a rash)
It goes away
Biopsy: eosinophils
Diagnosis? Does it go away?

Strawberry hemangioma
They can fade away
Diagnosis? What causes it? How does this differ from milia?
Neonatal acne
Caused by MATERNAL androgens in newborn
Differs from milia as it presents a week after birth where milia is present at the time of birth
Diagnosis? Does it go away? Treatment?

Nevus sebaceous
It does not go away
Can become malignant so need to remove that shit
Diagnosis? Treatment?
Seborrheic dermatitis
Clean with mild shampoo and/or antifungal
What two genetic disorders are contraindications for breast feeding
PKU
Galactosemia
Both Phenylalanine and galactose are found in breast milk
What is physiologic jaundice?
jaundice that occurs in newborns as their liver conjugation is not yet mature
What is breast feeding jaundice?
Misnomer. Should be called “Lack of breast feeding” jaundice.
Decreased feeding -> dehydration -> retain meconium and reabsorb deconjugated bili
What is breast milk jaundice?
Breast milk has glucuronidase which increases deconjugated bili in intestines and increased reabsorption
What is pathologic jaundice? What test do you order if you suspect pathologic jaundice? What if this test is positive?
Pathologic is if on 1st day of life, total bilirubin is greater than 12, DIRECT bilirubin >2, and/or rate of rise >5/day
Order a coombs test
Positive: Rh or ABO incompatability
A 7 day old baby has dark urine, pale stools, total bili~12, direct bili 8, and elevated LFTs. What is the diagnosis? Treatment?
Biliary atresia
Surgery (some require liver transplantation)
What is the main difference in Dubin Johnson and Rotor disease?
Dubin Johnson = black liver
Rotor = no black liver
A baby is born with respiratory distress, scaphoid abdomen, and this XRAY. What is the diagnosis? What is the major concern? What is the treatment?

Diaphragmatic hernia
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Surgery
A baby is born with respiratory distress with excessive drooling. Also coughs when feeding. What is the diagnosis? What is the best test to diagnose? What other physical exam findings should you look for?
TE-fistula
Place feeding tube then XRAY to see it coiled in thorax
VACTERL (Vertebral, Anal atresia, Cardiac, TE fistula, Renal, and Limb anomolies)


