Pelvic Viscera Blood Supply and Nervous Innervation Flashcards
(42 cards)
Neurovascular organization of the pelvis:
- NVA runs within endopelvic fascia.
- Arranged in concentric layers, lateral to medial: SVA
- somatic nerves (lateral)
- blood vessels
- autonomic nerves (medial)

Label all:
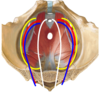
- NVA of pelvis; lateral to medial: SVA
- somatic nerves (yellow)
- blood vessels (blue/red)
- autonomic nerves (white)
Label all:


Largest nerve passing through the greater sciatic foramen:
- sciatic nerve (L4-S3). Joins with the lumbosacral trunk before exiting.
Route of lumbosacral trunk to it union with the sciatic nerve:
crosses over pelvic brim
Somatic nerves making up the lateral component of the pelvic neurovasculature are the:
- obturator nerve, sciatic nerve, and pudendal nerve.
- Lumbosacral trunk passes over the pelvic brim to unite with sciatic.
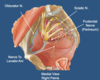
Label all:


Primary blood supply to pelvic structures:
- arterial: branches of internal iliac artery
- venous: branches of internal iliac vein
The two trunks of the internal iliac artery and their target blood supply:
- posterior division: blood supply to pelvic body wall.
- anterior division: blood supply to pelvic viscera.
The superior gluteal artery typically passes posteriorly between what two structures to enter the gluteal region from the pelvis?
- lumbosacral trunk and S1
The inferior gluteal artery typically passes from the pelvis to the gluteal region by exiting between what two structures?
- piriformis and coccygeus, typically between S2 and S3.
Lymphatics of the pelvis follow along what structures:
- vasculature of the respective pelvic viscera.
- ovary = ovarian artery (branch of abdominal aorta)
- uterus = uterine artery (branch of internal iliac)
Blood supply to ovary and derivation:
- ovarian artery.
- branch of abdominal aorta near kidney level.
Blood supply to cervix/uterus and derivation:
- uterine artery.
- branch of internal iliac artery.
How will ovarian cancer metastasize?
- follow vasculature (ovarian artery and vein).
- spread along the lateral aortic lymph nodes.
How will cervical cancer metastasize?
- follow vasculature (uterine artery).
- spread along internal iliac lymph nodes.
Two important characteristics of the uterine arteries:
- pass superior to ureter (“water under the bridge”).
- course within transverse cervical (cardinal) ligaments.
Function of pelvic sympathetic nervous innervation (3):
- vasoconstriction of pelvic arteries
- contraction of smooth muscle sphincters
- (Males) peristalsis of sperm through vas deferens
The two sphincters controlled by pelvic sympathetic nervous innervation and effect of this innervation:
- internal urethral sphincter.
- internal anal sphincter.
- Sympathetics keep tonically closed so can fill.
Function of pelvic parasympathetic nervous innervation (3):
- contraction of detrusor muscle (bladder excretion).
- rectal peristalsis.
- inhibit smooth muscle sphincters (urethral and anal).
How are the internal urethral sphincter and internal anal sphincter relaxed so that they can be emptied?
- parasympathetics inhibit sympathetic tonic contraction of these sphincters.
- sphincters then relax.
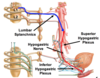
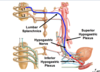
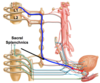
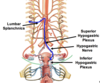
Label all (pelvis):
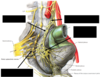

Location of PREganglionic sympathetic cell bodies innervating the pelvic visecera:
lateral horn L1 and L2.
Location of POSTganglionic sympathetic cell bodies innervating the pelvic visecera:
- superior mesenteric plexus
- inferior mesenteric plexus
- inferior hypogastric plexus