pelvis A Flashcards
(151 cards)
What are the 4 portals for portal hyerptension
Left/right gastric vv , superior mesenteric v, inferior mesenteric v, paraumbilical v

Where does the left/right gastric vv drain back to? and what organ does it effect if there is portal hypertension? (verices)
Esophageal v, to the Azygos to the SVC. Esophagus
Where does the superior mesenteric v drain back to? and what organ does it effect in portal hypertension (verices)
Colic vv, tp the ascending lumbar v to the SVC. colon
Where does the inferior mesenteric v drain back to? and what organ does it effect in portal hypertension? (verices)
Superior rectal v, middle/inferior rectal vv, IVC. rectum
Where does the paraumbilical v drain back to? and what organ does it effect in portal hypertension? (verices)
periumbilical vv, inferior epigastric v, IVC. umbilicus
Differences in male and female pelvis. MALE
Heavy bones, heart shaped pelvic inlet conical pelvic cavity ant/post oval pelvic outlet narrow (90 degrees) infrapubic angle narrow and deep iliac fossa
Differences in male and female pelvis. FEMALE
Light bones oval pelvic inlet cylindrical pelvic cavity circular pelvic outlet wide (120 degrees) indrapubic angle wide and shallow iliac fossa
what is Levator Ani muscle
puborectalis, m puboococcygeus m iliococcygeus m. floor of the pelvis with pelvic diaphram. same in both sexes except females with have another hiatus for vagina

what is pelvic diaphragm?
levator ani mm + coccygeus m. floor of the pelvis.

what is the pelvic outlet? what perineum triangles are in the pelvic outlet
the inferior hole of the pelvis. urogenital triangle and anal triangle

what is in the urogenital, and anal triangle? which one is more superior?
Perineum. urogenital is more superior.

what makes up the anal triangle?
sacrotuberous ligaments, sacrum, and imaginary line between the two triangles

what makes up the urogenital triangle?
ischiopubic rami and imaginary line

which anal sphincter is voluntary?
external

which anal schinter is controled by autonomics?
Internal anal sphincter

which autonomics is the internal anal sphincter innervated by?
pelvic and sacral sphlanchnic
what nerve is the external anal sphincter innervated by?
pudendal nerves. somatic
how many transverse folds do we have in the rectum? what do they do?
2 on the left 1 on the right
gives rise to the curvature of the pelvis
ischioanal fossa is filled with what?
it is a fat filled space

what muscle is the internal pudendal vasculature and pudendal nerve closely associated with?
obturator internus muscle

what is the round ligament anaolgous to in males?
inferior scrotal ligament. a remnant of the gubernaculum. it is a content of the inguinal canal in females but is usally obliterated.

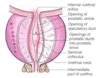
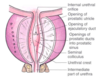
bladder, uterine and rectum… which ones are anterior middle and posterior?
anterior: bladder
posterior: rectum
middle: uterus
Deep pouch is surounded by?
superior UG fascia. and inferior UG fascia aka perineal membrane.

what is the superfical pouch surounded by?
a fascia of perineum and the perineum membrane