Perineum 1 & 2 Flashcards
(77 cards)
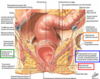
The perineum is the region of the trunk below the pelvic diaphragm and bounded by the pelvic outlet. It is subdivided by a line connecting the ischial tuberosities into 2 triangles that do not communicate. They are:
–anterior urogenital triangle(horizontal)
–posterior anal triangle (almost vertical)

What is the innervation and nerve supply of the perineum?
- Main innervation: pudendal nerve
- Main blood supply: internal pudendal artery & internal pudendal vein
The urogenital triangle consists of what 5 things?
- Skin
- Superficial fascia
- Superficial perineal pouch
- Perineal membrane
- Deep perineal pouch

The Superficial fascia of the urogenital triangle consists of 2 layers, a fatty layer and a membranous layer known as……………….
Colle’s fascia
The superficial perenial pouch is located between the colles’s fascia and the perineal membrane. It does what?
anchors external genitalia

The deep perineal pouch is located between the pelvic diaphragm and the perineal membrane. It includes what important structure?
external urethral sphincter
What 3 things make up the anal triangle?
- Skin
- Superficial fascia (fatty layer that extends into the ischio-anal fossa)
- Anal canal surrounded by the external anal sphincter

The pudendal nerve & internal pudendal vessels are the main nerve & blood supply of the perineum. The pudendal nerve leaves the pelvis through the…………. and enters the perineum through the………………
greater sciatic foramen
lesser sciatic foramen

Inferior to the………………., the pudendal nerve enters the…………………. canal formed from the obturator internus fascia (below pelvic diaphragm) to travel in lateral wall of ischioanal fossa. It is accompanied by the internal pudendal artery and vein.
ischial spine
pudendal

What kind of nerve is the pudendal nerve?
a mixed somatic nerve
What are the parts that make up the pudendal nerve (which is a mixed somatic nerve)?
- Inferior rectal nerve to the external anal sphincter and levator ani (GSE) and perianal skin (GSA)
- Perineal nerve
- Dorsal nerve of the penis or clitoris, which is sensory (specially to glans) (GSA)

The perineal nerve (a part of the pudendal nerve) divides into what 2 nerves?
- Cutaneous posterior scrotal or labial branches (GSA) which goes to posterior scrotum or labia.
- Deep perineal nerve (GSE) which goes to skeletal muscles of the superficial and deep perineal pouches, including the external urethral sphincter/skin of vestibule, and mucosa of lower vagina (GSA)
Visceral innervation of the perineum comes from what?
- Branches of the pudendal nerve (SYMPATHETIC)
- Inferior hypogastric plexus (SYMPATHETIC AND PARASYMPATHETIC)
Branches of the pudendal nerve are sympathetic fibers (L1-2) which go to what?
- Skin of perineum (vessels, sweat glands, hair erector muscle)
- Vessels of skeletal muscles of perineum & mucosa of lower anal canal
- Erectile tissues of penis & clitoris
The Inferior hypogastric plexus has sympatheic and parasympathetic fibers that supply what?
- Sympathetic fibers (L1-2) to blood vessels of upper anal canal, internal anal sphincter, membranous urethra
- Parasympathetic fibers (S2-4) to blood vessels of upper anal canal, internal anal sphincter, membranous urethra, glands of reproductive system/erectile tissues of penis & clitoris (cavernous nerves)
- GVA fibers with parasympathetic fibers (S2-4)
What are the Internal Pudendal Artery Branches?
- Inferior rectal artery (Anal canal & sphincters)
- Perineal artery
- branches to Posterior scrotal or labial arteries.
• Terminal branches
- Artery to the bulb of the penis or vestibule
- Deep artery of the penis or clitoris
- Dorsal artery of the penis or clitoris

Which artery is essential for erection?
Deep artery of the penis!
* The deep artery of the penis or clitoris each enters a crus (corpora cavernosa).

What are the Internal Pudendal Vein tributaries?
- Inferior rectal vein
- Posterior scrotal or labial vein
- Vein to the bulb of the penis or vestibule

What are the exceptions to the tributaries of the Internal Pudendal Vein (meaning the veins that dont feed into the internal pudendal vein)?
- Deep dorsal vein of penis or clitoris: drains glans & corpora cavernosa; drains in prostatic plexus (male) or vesical plexus (female) of veins.
- Superficial dorsal vein of the penis or clitoris: drains corpus spongiosum, urethra, fascia & skin of penis in external pudendal vein (femoral vein)

Lymph Drainage from the Perineum is mainly to the superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes, with important exceptions:
- The testis drains to lateral aortic nodes in the abdomen.
- Some lymph vessels follow the round ligament of the uterus from the uterus to the labium majus, which then drains to superficial inguinal nodes.
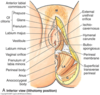
The Ischio anal fossa is filled with fat & loose connective tissue. It is bordered by skin, gluteus maximus, obturator internus and fascia, levator ani and fascia, and external anal sphincter.
On the lateral wall is the…………… containing the…………….
Pudendal canal
pudendal nerve & vessels

Crossing the ischioanal fossa are the…………………..
inferior rectal nerves and vessels (branch from pudendal n. and internal pudendal a. and v. at the sciatic notch)

What is important to note clinically about the Ischioanal fossae?
It is a common site for abscess formation. An infection in one ischioanal fossa may spread behind the anal canal into the other ischioanal fossa.

The anal canal is surrounded by what 3 things?
- Internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle)
- External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle)
- Fat of the ischioanal fossa