PF Flashcards
(39 cards)
What are the four layers of the pelvic floor?
What are their main functions?
- Anal sphincter (with puborectalis, provides fecal continence - Sphincteric)
- Superficial Genital muscles (Sexual function)
- Perineal Membrane (urinary continence - Sphincteric)
- Pelvic Diaphragm – also called Levator Ani (support)
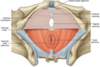
What muscles makes up the Anal sphincter?
Internal Anal Sphincter (smooth muscle)
External Anal Sphincter (skeletal muscle)
What are considered the superficial layers of the pelvic floor? (in order of most superficial to least superficial if you want)
- Anal sphincters (with puborectalis, provides fecal continence - Sphincteric)
- Superficial Genital muscles (Sexual function)
- Perineal Membrane (urinary continence - Sphincteric)
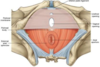
What are considered the deep layers of the pelvic floor?
- Pelvic Diaphragm – also called Levator Ani (support)
In which pelvic floor layer does dysfunction mainly occur in?
- Pelvic Diaphragm – also called Levator Ani (support)
What are the names of the two anal sphincters? What type of muscle are they?
Internal Anal Sphincter (smooth muscle)
External Anal Sphincter (skeletal muscle)

What are the three muscles of the Superficial Genital Muscles?
- ischiocavernosus
- Bulbocavernosus
- Superficial transvers perineal

What are the three muscles of the Perineal Membrane?
- Urethrovaginal sphincter
- Compressor urethrae
- Sphincter Urethra
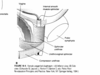
What are the four muscles of the Pelvic Diaphragm?
- Coccygeus
- Illiococcygeus
- Pubococcygeus (also called pubovaginalis)
- Puborectalis
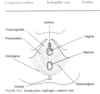
Which muscle is considered the “tail wagger”?
Coccygeus (part of pelvic diaphragm)
*may stabilize the sacrum

Which muscle slings around the vagina?
Pubococcygeus (also called pubovaginalis) (part of the pelvic diaphragm)

Which muscle slings around the rectum?
Puborectalis (part of the pelvic diaphragm)

What 2-3 muscles provide fecal continence?
Anal Sphincters (internal and external) with the puborectalis from the pelvic diaphragm (it slings around the rectum)

What are 4 sort-of phases of micturition? What is a fourth thing we talked about that is not really a phase?
- Storage
- Transition-phase
- Emptying
- (Post-Void) – nota true phase
Describe sensations during the bladder storage stage:
(include volumes)
- When bladder is 150 mlfull, the person gets the “first sensation” to urinate
- When bladder is 200-300 ml full, it increases activation of bladder stretch receptors which increases urge to urinate
- When bladder is 400-550 ml full, the urge to urinate is severe
What is the detrusor doing during the bladder storage stage?
Quiet/relaxed
What is the Pelvic floor doing during the bladder storage stage?
Contracts minimally to maintain resting tone
What happens during the bladder transition phase?
Person decides it is time to take action.
Transport to toilet, remove clothes.
What happens to the detrusor muscle and pelvic floor muscles during the emptying bladder phase?
Detrusor contracts (no increase in intra-abdominal pressure!)
Pelvic Floor Relaxes
Is it normal to have some urine in the bladder post-void? If so, how much?
A bit of urine is okay. Dr. Mincer’s chart listed 0-50 ml. I think Dr. T said up to 30 ml
Normal Micturition: What sensation is present post-void?
No urge
What does the detrusor muscle and pelvic floor muscles do post void?
Go back to
- Relaxed Detrusor
- Pelvic floor has normal resting tone.
What is one way your body can delay voiding if you have a strong urge but are not close to a toilet?
The pelvic floor may contract harder to delay voiding. This also inhibits the detrusor from contraction by activating a reflex.
You can do this on purpose or teach a pt to do this on purpose.
Explain what the detrusor does during the stages of normal micturition:
Detrusor is relaxed except during emptying