PHYS 5 The adrenal gland Flashcards
(40 cards)
what does each zone secrete?

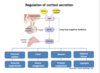
Axes with adrenal gland is?
under what control? via?

cortisol secretion
stimulated by?
what type of feedback does cortisol do?
effects what tissues? effect on each?
circadian rhythm of cortisol
when is it high? low?

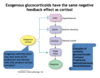
exogenous glucocorticoids have what feedback?
exogenous administration can cause what to happen?
ex of synthetic glucocorticoids?
regulation of aldosterone secretion
secretion caused by what pathways?
stims what part of adrenal cortex?

Symptoms and signs of Cushing’s syndrome

tests for cushing syndrome/disease?
L- tells what? doesn’t tell?
H- tells us what?

consequences of glucocorticoid excess
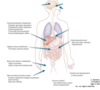
HPA axes for 3 different tumors what happens to the hormones at each level?
1 with exogenous glucocorticoid administration

etiologies of Cushing’s syndrome
(4 main types)

High-dose dexamethasone suppression test
tells us what? why?

Plasma ACTH concentration in patients with Cushing’s syndrome
CD- level?
AT- level?
EA- level?

primary action of aldosterone is?
aldosterone gets receptor where?
after binding what happens?
this allows what to happen?
existing pumps?
result is?

ACTH
produced where?
derived from?
type of hormone?
ACTH can then be broken down into?

what may you see in Addison’s disease?
perhaps due to melanin from ACTH

use what test to detect adrenal gland insufficiency?
how would you do this?
what are the possibilities?

normal HPA axes release?

1st degree adrenal insufficiency
HPA axes?
what is wrong?

2nd or 3rd degree adrenal insufficiency
HPA axes?
effect?

causes of 1st-degree adrenal insufficiency
(______ disease)
(4)
what can cause two of these causes to happen?

treatment of adrenal insufficiency
usually treated by?
in 2nd degree?



aldosterone pathologies
Hyper- types? name of a syndrome?
Hypo- causes? (3)