Porth: Chpt. 28 Flashcards
(170 cards)
What is the GI Tract also referred to as?
- Digestive Tract
- Alimentary Canal
- Gut
What is the Intestinal Portion of the GI Tract called?
- Bowel
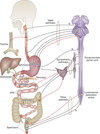
Name the Accessory Organs that produce secretions & aid in digestion?
- Pancreas
- Liver
- Salivary Glands
Major Physiologic Functions of the GI Tract
- Digest food
- Absorb nutrients
How does the GI Tract carry on the functions of digestion & absorption?
- Motility
- Secretion
- Digestion
- Absorption
What happens to the Unabsorbed Nutrients & Wastes in the Large Intestine?
- Collected
- For later elimination

What must Nutrients do in order to become part of the body’s Internal Environment?
- Pass through Intestinal Wall
- Enter Blood & Lymph Channels
For Simplicity’s Sake:
What are the 3 parts of the GI Tract?
- Upper part
- Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach
- Intake source & Receptable
- 1st portion of digestive process
- Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach
- Middle part
- Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
- Digestion & Absorption!
- Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
- Lower part
- Cecum, colon, recturm
- Storage channel
- Elimination of waste
- Cecum, colon, recturm
Which President signed Father’s Day into Law?
- 1966, President Lyndon B. Johnson issued the first presidential proclamation honoring fathers, designating the third Sunday in June as Father’s Day.
- Six years later, the day was made a permanent national holiday when President Richard Nixon signed it into law in 1972.
What does Saliva do?
- Moisten & lubricates food
- Eaiser to Swallow
- Enzymes
- Initial digestion of Lipids and Starches
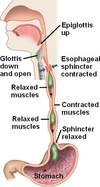
The Esophagus
- 25cm, straight, collapsible tube
- Connects oropharynx w/ stomach
- Conduit for passage of food
- Smooth muscle = Peristalsis!
- Mucosal/Sub-mucosal glands = Protects surface, lubricates food
The Esophagus
&
Its Sphincters
- 2: Upper & Lower
-
Upper = pharyngoesophageal
- Striated muscle
- Keeps air from entering stomach
-
Lower = gastroesophageal
- Circular muscle
- Tonically contracted
- Zone of high pressure
- Prevents reflux
- Passes through hiatus in diaphragm to join w/ stomach
-
Upper = pharyngoesophageal
The Esophagus
&
“Receptive Relaxation”
-
Lower = gastroesophageal sphincter
- Allows propulsion of esophagus contents into stomach
- Hiatus region = high pressure
- Prevents reflux

The Stomach
-
Pouchlike structure
- Food storage reservoir
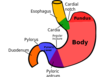
The Stomach
+
Cardiac Orifice
Where esophagus opens into stomach

The Stomach
+
Pyloric Sphincter
End of pyloric canal
Circular, Smooth muscle
Valve = controls rate of stomach emptying
+ Prevents regurgitation of intestinal contents into stomach
Middle GI Tract
-
Duodenum:
- 22cm long
- Connects Stomach to Jejenum
- Opening for Common Bile Duct + Main duct
- Juices enter via ducts
-
Jejunum & Ileum:
- 7m (23ft) long [folded]
- DIGESTION & ABSORPTION!
Lower GI Tract
- Large intestine = 1.5m (5ft) long
- Cecum, Colon, Rectum, Anal Canal
- Cecum = Pouch @ junction btwn Ileum & Colon
- Valves - prevent return of feces into small intestine
- Appendix = 1in from ileocecal valve
- Colon
- Descending colon extends to rectum
- Rectum = sigmoid colon to anus
- Anal Canal = btwn levator ani muscles
- Spinchter muscles = no incontinence
How fast does a crack in glass travel?
When glass breaks, the cracks move faster than 3,000 miles per hour!!!
GI Wall Structure
The Digestive Tract is a __________ tube

-
Four-Layered Tube
- Inner Mucosal Layer
- Epithelium, Lamina propria, Muscularis mucosa
- Submuscosal (2nd layer)
- Connective & Adipose
- Muscularis externa (3rd layer)
- Serosal (4th layer)
- Mesothelium (squamous)
- Inner Mucosal Layer
GI Wall Structure
Inner Mucosal Layer - Functions
- Lubricates & Protects inner surface of alimentary canal
- Secretes digestive enzymes
- Break down food
- Absorb breakdown products
- Prevents entry of bad substances
- Lymphatics in here = 1st line of defense
GI Wall Structure
Inner Mucosal Layer - Epithelial Lining
- Rapid turnover rate
- Replaced q 4-5 days
- Heals rapidly
- No scar tissue
GI Wall Structure
Second Layer - Function
- Secretes digestive enzymes
- Has lots of vasculature
GI Wall Structure
Third Layer - Function
- Circular smooth muscle cells
- AND
- Longitudinal smooth muscle cells
- =’s
- Facilitate MOVEMENT of GI Tract contents
- =’s