Posterior Thigh and Knee Anatomy Flashcards
(103 cards)
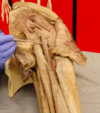
What region is being pointed to?
Ischial tuberosity

What muscles originate from the ischial tuberosity?
The hamstrings
Is this a left or a righ femur?

Left - anterior aspect
What is being pointed to?

Medial and lateral lips of linea aspera
What muscles are attached to the linea aspera?
- Some of the quadriceps muscles (anterior)
- Some of the adductor muscles (medial)
- Short head of biceps femoris (posterior)
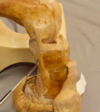
What is being pointed to? What does it articulate with?

Femoral condyles (medial and lateral) - articulate with tibial plateaus
What structure is being pointed to? (anterior surface of distal femur)
Adductor tubercle
What attaches to the adductor tubercle?
Hamstring part of adductor magnus
What is being pointed to?

Tibial plateaus
What raised up area of bone is being pointed to?
Intercondylar eminence
What is found anterior and posterior to the intercondylar eminence on the tibia?
Attachment sites for cruciate ligaments
What is being pointed to? What is this an attachment site for?

Tibial tuberosity - attachment site for quads via the patella tendon
Which nerve wraps around the area being pointed to?

The common fibular nerve wraps around the fibular neck
Muscles of the posterior thigh generally act as…
- Hip extensors
- Knee flexors
What is the action of the short head of biceps femoris?
Flex the knee
What is the action of the hamstring part of adductor magnus?
Extends the hip
What nerves innervates the muscles of the posterior thigh?
Tibial nerve and common fibular (this innervates short head of biceps femoris)
What muscle is being pointed to?

Gluteus maximus
What is being pointed to?

Iliotibial tract (most laterally)
What muscle is this?

Gracilis (most medial)
What small triangular muscle in the gluteal region is being pointed to?

Piriformis
What bony landmark is being pointed to?

Ischial tuberosity
What nerve is being pointed to? How does it emerge in relation to piriformis?

Sciatic nerve - emerges inferiorly to piriformis
What ligament is being pointed to?

Sacrotuberous ligament