Practice Test w/pic Flashcards
(177 cards)
At the suprascapular notch, the suprascapular artery typically passes directly _______ to the transverse scapular ligament
Anterior
superior
posterior
inferior
Superior
At the suprascapular notch, the suprascapular artery typically passes directly _______ to the transverse scapular ligament
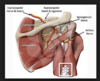
The posterior longitudinal ligament is positioned _______ to the spinal cord
medial
lateral
anterior
posterior
Anterior
The posterior longitudinal ligament is positioned _______ to the spinal cord
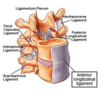
As the femoral artery (external iliac) exists the pelvis, it is positioned _____ to the inguinal ligament and _____ to the
iliopsoas muscle
anterior/anterior
anterior/posterio
posterior/anterior
posterior/posterior
Posterior/anterior
As the femoral artery (external iliac) exists the pelivs, it is positioned posterior to the inguinal ligament and anterior to the

The inferior gluteal nerve exits the greater sciatic nerve directly __________ to the piriformis muscle.
superior
inferior
medial
lateral
inferior
The inferior gluteal nerve exits the greater sciatic nerve directly ______ to the piriformis muscle

With the popliteal fossa, the popliteal artery is positioned directly ______ to the popliteus muscle
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Posterior
With the popliteal fossa, the popliteal artery is positioned directly ______ to the popliteus muscle
The tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes _____ to the lateral malleolus prior to attaching in part to the lateral aspect of the base of the 1st metatarsal
anterior-superior
anterior-inferior
posterior-superior
posterior-inferior
posterior-inferior
The tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes _____ to the lateral malleolus prior to attaching in part to the lateral aspect of the base of the 1st metatarsal
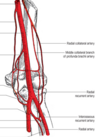
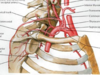
The subclavian artery and vein pass _____ to the clavicle
anterior-superior
anterior-inferior
posterior-superior
posterior-inferior
posterior-inferior
The subclavian artery and vein pass _____ to the clavicle
The radial nerve passes directly ____ to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus
anterior
posterior
superior
inferior
anterior
The radial nerve passes directly ____ to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus

The axillary artery and cords of the brachial plexus pass directly _____ to the pectoralis minor muscle
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Posterior
The axillary artery and cords of the brachial plexus pass directly _____ to the pectoralis minor muscle
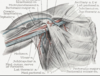
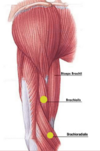
The radial nerve and profunda brachii artery pass directly ______ to the shaft of the humerus
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
posterior
The radial nerve and profunda brachii artery pass directly ______ to the shaft of the humerus
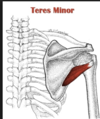
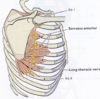
The long thoracic nerve is positioned directly _______ to the serratus anterior muscle
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Lateral
The long thoracic nerve is positioned directly _______ to the serratus anterior muscle
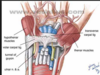
The ulnar nerve and superior ulnar collateral (or posterior ulnar recurrent) artery pass directly ______ to the medial epicondyl of the humerus
anterior
posterior
superior
inferior
Posterior
The ulnar nerve and superior ulnar collateral (or posterior ulnar recurrent) artery pass directly ______ to the medial epicondyl of the humerus

Near the wrist, the radial artery is positioned directly _____ to the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.
Medial
lateral
superficial
deep
Lateral
Near the wrist, the radial artery is positioned directly _____ to the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.

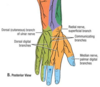
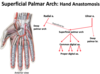
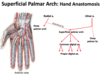
The ulnar artery and nerve pass directly _____ to the transverse carpal ligament.
Superficial
deep
superior
inferior
Superficial
The ulnar artery and nerve pass directly _____ to the transverse carpal ligament.
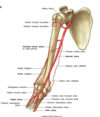
The radial artery passes directly ______ to the trapezium and base of the first metacarpal.
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Posterior
The radial artery passes directly ______ to the trapezium and base of the first metacarpal.
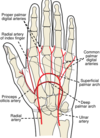
The tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle passes directly ____ to the dorsal tubercle of the radius.
Superior
inferior
medial
lateral
Medial
The tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle passes directly ____ to the dorsal tubercle of the radius.

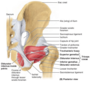
The obturator externus muscle passes directly _____ to the neck of the femur
Anterior
posterior
superior
inferior
posterior
The obturator externus muscle passes directly _____ to the neck of the femur
During its posterior course, the medial circumflex femoral artery passes directly ___ to the pectineus muscle
Medial
lateral
superior
inferior
Lateral
During its posterior course, the medial circumflex femoral artery passes directly ___ to the pectineus muscle
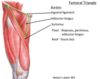
Immediately inferior to the inguinal ligament, the femoral nerve is positioneddirectly __________ to the femoral artery.
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Lateral
Immediately inferior to the inguinal ligament, the femoral nerve is positioned directly __________ to the femoral artery.

The median nerve and tendons of the FDS and FDP muscles all pass directly__________ to the transverse carpal ligament.
Superficial
Deep
Superior
Inferior
Deep
The median nerve and tendons of the FDS and FDP muscles all pass directly__________ to the transverse carpal ligament.

As they exit the greater sciatic foramen, the superior gluteal nerve, artery and vein arepositioned __________ to the piriformis muscle.
A. superior B. inferior C. medial D. lateral
Superior
As they exit the greater sciatic foramen, the superior gluteal nerve, artery and vein arepositioned __________ to the piriformis muscle.

The obturator internus tendon passes directly __________ to the neck of the femur.
A. anterior B. posterior C. medial D. lateral
Posterior
The obturator internus tendon passes directly __________ to the neck of the femur.

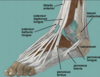
The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle passes directly __________ to thesustentaculum tali of the calcaneus.
A. anterior B. posterior C. superior D. inferior
Inferior
The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle passes directly __________ to thesustentaculum tali of the calcaneus.

The tibial nerve passes directly __________ to the medial malleolus.
A. anterior B. posterior C. medial D. lateral
Posterior
The tibial nerve passes directly __________ to the medial malleolus.