Principles of fractures Flashcards
(20 cards)
When assessing a patient with a fracture, what’s the most important aspect to consider?
If there is soft tissue injury
how do you describe the location of a fracture in a long bone? what terminology ?
in 1/3rds, ie proximal, middle or distal third
There are many fracture configurations, name 4
Transverse
Oblique
Comminuted
Spiral
Segmental
Avulsion
Compression
Torus
Greenstick
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?

transverse
due to a direct blow (most commonly an injury to the ulnar from protecting yourself in a fight from a baton)
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?

oblique fracture
due to a bending force
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?
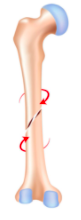
spiral fracture
due to a rotational force
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?

comminuted fracture
high energy injury
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?

segmental
due to a high energy injury
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?

Avulsion fracture
musculo-tendinous pull off
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?
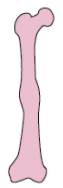
torus fracture
low energy - usually in children
Describe the fracture configuration in this picture.
what is the cause of these injuries?

greenstick fracture
when considering fracture displacement, what are the different types of displacement?
- undisplaced
- angulated (distal portion angled in relation to proximal e.g. dorsally or volar)
- translated (medio-lateral or anterior-posterior shift)
- shortened
- rotated (usually seen clinically e.g. femoral neck fracture causes external rotation)
what are the risks associated with open fractures?
infection, non-union, malunion
what is the immediate treatment for open fractures?
urgent debridement, reduction and immobilisation
list 3 risks of intra-articular fractures if joint congruity is not restored
- joint pain
- stiffness
- post-traumatic osteoarthritis
what is the treatment for intra-articular fractures?
reduction and rigid fixation
what are the 3 basic Rs of fracture management
Reduce (to realign the fragments)
Retain (immobilise)
Rehabilitate
what are the methods of conservative and surgical immobilisation of a fracture?
conservative: splint, sling, cast
surgical:
- smooth wires (k-wires)
- intramedullary nail
- plate and screw
- external fixator (cage thing)
list 4 complications of fractures
- compartment syndrome
- non-union
- malunion
- infection
what are the 2 main types of non-union and what might the reasons for these be
atrophic:
- smoking
- malnutrition
- immunocompromised
hypertrophic: failure of immobilisation


