PSA and Thyroid Hormones Flashcards
(40 cards)
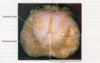
Region Specific Prostate Pathologies
(2)
BPH - 90% of cases develop in transition zone
Prostate cancer - 70% of cases develop in peripheral zone
Major Prostate Gland Disorders
(3)
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Prostatitis
- Prostate cancer (ex - prostatic adenocarcinoma)
Prostate Cancer Epidemiology
- Most commonly diagnosed solid tumor
- Second-most common cause of death due to malignancy in US males
- 233,000 projected new cases and 29,400 projected deaths in 2014
American Urological Society Clinical Staging - Prostate Cancer

PSA Structure and Prdctn
- **Structure: **Glycoprotein, functions as serine protease in the kallikrein amily (also hk3)
- Produced by epithelial cells in prostatic acini and ducts, secreted into seminal fluid
PSA Synthesis
Note - some labs allow you to order any of these trunchated or native forms

PSA-Containing Fluids
(7)
- Semen
- Male serum
- Amniotic fluid
- Breast milk
- Saliva
- Female urine
- Female serum
Serum PSA Forms
(2, 1 c 3 specifics, include relative amounts)
- Free, unbound form (~ <30%)
- Bound to serine protease inhibitors (~ >70%)
- α1-antichymotrypsin (ACT)
- α2- macroglobulin (A2M)
- α1-protease inhibitor (API) - 0.5-2%
Note - you can test either of these
PSA Evaluations to Dec. Biopsy Incidence
(3)
- PSA density – is an adjustment that divides the PSA measurement by the gland volume.
- fPSA/total PSA or tPSA ratio
- PSA velocity – monitors the change in PSA with time.
- Greater than 0.75 ng/mL per year is suggestive of cancer
PSA Assays
(3)
- tPSA - measures free and complex forms, primarily ACT
- Free PSA
- Complex PSA - rarely used
Conventional PSA Level Indicating “Low Risk” for Cancer
tPSA < 4.0 ng/ml
PSA Level and Cancer Risk
- 2.6 ng/ml for low risk
- 4 – 10 ng/ml represents diagnostic gray zone
- > 10 ng/ml greater likelihood of cancer
Note - Mayo Clinic has its own system, attached

Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
(3)
- Black race
- Family hx
- High fat/low vegetable diet
Prostate Cancer Prevention
Annual PSA and DRE after age of 50 (40 if high risk)
Prostate Cancer Clinical Presentaiton
- Most common is asymptomatic elevation in PSA
- DRE findings of asymmetric indurations (hardening) or nodules are suggestive.
- Less common are obstructive symptoms, new onset ED, hematuria or hematospermia
%fPSA
(define, calculation)
Free-to-Total PSA ratio
Calculation:
fPSA/tPSA x 100 = %fPSA
*Note - the lab will do this for you *
%fPSA Interpretation
- Men without PCa have a higher ratio (>25%) of free to tPSA
- %fPSA of < 25% detected 95% of PCa when tPSA is between 4 – 10 ng/ml.
- 20% of patients with tPSA between 2.6 – 4.0 ng/ml have significant PCa. Using a cutoff of 27% fPSA detected 90% of cancers.
*Note - good dx tool but there are a lot of assumptions associated c it *
Age Adjusted PSA Ranges, Caucasian Males
0-2.5 aged 40-49 years
0-3.5 aged 50-59 years
0-4.5 aged 60-69 years
0-6.5 aged 70-79 years
Specificty of these adjustments = 95%
Age Adjusted PSA Ranges, Black Males
0-2 for men aged 40-49 years
0-4 for men aged 50-59 years
0-4.5 for men aged 60-69 years
0-5.5 for men aged 70-79 years
*Specificity ranges from 78% in older men - 93% in younger men *
PSA Screening Requirement
after they receive information about the uncertainties, risks, and potential benefits associated with prostate cancer screening
PSA Assay Labels
(2)
- Chemiluminescent labels
- Fluorescent labels
*Note - these do not include the high (analytical) sensitivity (hs) assays that are used for extenuating circumstances *
Prostate Cancer Tx
- Early stage disease
- Radical prostatectomy
- External beam radiation
- Brachytherapy (use of radioactive implants at the treatment site)
- Locally advance disease
- Can be treated with a combination of surgical, radiation, and hormonal therapy.
- Metastatic disease
- Is incurable but and can be managed with hormonal therapy for 2-10 years
Thyroid Gland Structure
Gross Structure
- 2 lobes
- thin connecting isthmus
Functional Components
- Follicles - secretory units
- Colloid - amorphous material composed of thyroglobulin and iodinated thyroalbumin
- Parafollicular/C cells - calcitonin
Thyroid Hormones
(list and describe 2)
- Hormones - T3 and T4*
- T3: biologically active thyroid hormone
- States in Circulation *
- Bound
- Thyroxin binding globulin (TBG)
- Thyroxin binding pre-albumin (TBPA)
- Albumin
- Free - correlates c functional thyroid state
- T3: 0.2 - 0.4%
- T4: 0.03%



