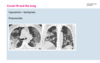
Pulmonary Diseases Flashcards
(33 cards)
What is evidence based medicine?
(EBM)

Form history to treatment
Explain the management rhythm

5 vital signs
- Without one of this signs = we can not life
Delivering bad/ serious new to a patient and their families
What is important?

Mortality rate from Tabacco in Switzerland
- 10 000 deaths/ years from tabacco = 15% of al deaths
Non communicable diseases (NCD)
You can not cure it = Prevention
–> Tell me 3 preventions

Anatomy Lunges

Function Lunge
- Gas exchange
- Protection against infection
Other:
- regulation of blood pressure
- speech
- filter out small blood clots from veins (stroke prevention)
Pathophysiology
Hypoxemia
Obstructive
restrictive lung disease
Hypoxemia
- Lack of oxygen
Obstructive
- The air can not go out of the lunges
restrictive lung disease
- Lungs are less capable

Respiratory pattern:
Bradypnea
Kussmaul
Cheyne Stokes

HYHA Classification
Dyspnea/Chest pain classification

Symptom Dyspnoea
What are the common causes?

Pneumonia
There are two different sorts?
- What is the difference?
- Mortality high or low?
Risk factors?

Pneumonia
Microbiology
- Tell me the two reasons to get Pneumonia?
- BUT = what is the problem?
- categories of the most common causes
- Bateria (Streptococcus pneumonia)
- Viruses ( Respiratory)
BUT 62% of cases nonpathogen

Pneumonia - Symptoms

Pneumonia
Diffrential diagnosis
Making the diagnosis - what are the signs & what can we measure?

Pneumonia
- Severity - test (screen)
- Complications

Pneumonia Treatment

COPD
Tell me the 3 conditions
What is the character of this disease?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a common respiratory condition
- Characterized by fixed airflow limitation
- Chronic bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Asthma

COPD
Symptoms
What is the most important risk factor?
- Dyspnea
- Chronic cough
- sputum production
Smoking 80% - (more than 40 pack years)
COPD Classifiaction

Treatment & Prevention COPD

COPD -Exacerbation
What happened?
Ris factors?
Triggers?
(Lungeninfakrt)
Die Atembeschwerden werden dann abrupt schlimmer. Solche Krankheitsschübe nennt man in der Fachsprache „Exazerbationen“. Auf einmal nimmt die Atemnot merklich zu. Man fühlt sich krank und leistungsschwach. Solche akuten Krisen können immer wieder im Verlauf einer COPD auftreten.
- An acute event - the function get wore
- Scute change in cough. sputum, Dyspnea