Radiology Exam #3 Flashcards
(56 cards)
Fracture of this anatomical structure is called?

Femoral Neck Fracture
(Broken Hip)

Identify the fracture in the Image

Displaced femoral neck fracture
(More Severe than standard femoral neck fracture)
Identify the Image
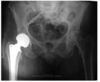
Hip Replacement
What type of fracture is depicted in the
image on the right? What is depicted on the
left image?

Comminuted Fracture
Intact Femoral Neck

What is a Communited Fracture?
A fracture where at least three separate pieces of bone are present
What is myositis osificans?
A process by which ossification of soft tissue
(usually muscle or tendon) abnormally occurs due to some cause.
What is being depicted in the Image?
What disease is it associated with?

Calcification (which is a part of ossification)
Mytosis Ossificans
Identify K.
What disease is being depicted in the image?
What is its cause?

K = Kidney
Bilateral Aseptic Necrosis of the Hips
Steroid Use or Trauma
Identify the disease associated with the Image

Aseptic Necrosis of the Left Femoral Head
Identify the disease depicted in the Image.

Bone Infarcts aka Avascular Necrosis
How do Bone Infarcts or Avascular Necrosis
Occur?
Sickle Cell disease or as a result of decompression
sickness after prolonged scuba diving.
What are bone Infarcts (aka Avascular Necrosis)?
Diffuse and amorphous calcification within the medullary space is seen here in the distal femur
Identify the disease associated with the image
below.
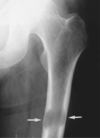
Lytic Bone Metastases
Identify the finding depicted in the image.

Pathological Fracture of the Femur
(Likely due to Lytic Bone Metastases)
Identify the finding indicated in the Image.

Knee Effusion
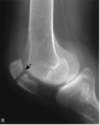
Identify the Finding Depicted in the Image

Patellar Fracture
Identify the finding depicted in the image.

Patellar Fracture
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Total Knee Replacement
(Semi-Constrained Prosthesis)
Identify the finding associated with the image
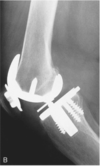
Total Knee Replacement
(Prosthetic Tricompartemnt)
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Tibial Fracture
Identify the finding assoicated with the Image.

Spiral Fracture of the Distal Tibia
(With override)
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Fracture of the proximal fibula (with override)
Identify the finding associated with the image.
(Which view)

Intermedullary fixation of a tibial fracture
(Lateral)
Identify the finding associated with the image.
(Which view)

Intermedullary fixation of a tibial fracture
(AP view)








































