radiology test Flashcards
(70 cards)
what is a greenstick fracture?
a partial thickness fracture where only cortex and periosteum are interrupted on one side of the bone but remain uninterrupted on the other.
Where are the most common sites for a greenstick fracture to occur?
They occur most often in long bones, including the fibula, tibia, ulna, radius, humerus, and clavicle.
what is a Salter–Harris fracture fracture?
A Salter–Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate or growth plate of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. It is a common injury found in children, occurring in 15% of childhood long bone fractures.
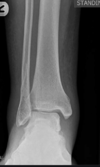
what is a buckle fracture?
a common fracture of the distal radius +/- ulna where only one side of the bone buckles but the other side of the bone is unaffected.
What does this image show?

a buckle fracture
What are the radiological findings for bronchiolitis?
air trapping - more than 5-6 ribs seen and flattened diaphragm on lateal cxr
A young girl became rapidly unwell and febrile with nosiy breathing. What does this image show?
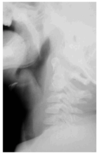
epiglottitis
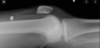
What does this image show?
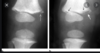
bucket/corner fracture - which is pathopgominic for peadiatric abuse/NAI
What does the term ‘periosteal reaction’ mean?
formation of new bone in response to injury
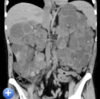
what does a mass arising from the kindey in a child usually indicate?
a Wilm’s tumour (nephroblastoma)
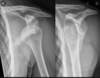
What is a Monteggia fracture dislocation?
a fracture of the proximal ulna or plastic deformation of the ulna with radial head subluxation/dislocation
What does this xray show?

A monteggia fracture of the ulna
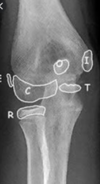
What does this x ray show?

a lateral condyle fracture of the humerus
what does this xray show?

a supracondylar fracture of the humerus
what does this xray show?

an olecranon fracture (which is part of the ulnar bone)
What is a Galeazzi fracture?
How do you remember the difference between Galeazzi and monteggia fractures?
GRUesome MURder
Galeazzi # has the radial bone fractured with ulnar dislocation
Monteggia # has ulnar bone # and radial dislocation
what does this image show?

an intertrochanteric #
What does this image show?

acetabular rim #
What are these fractures

subcapital
transcervical
intertrochanteric
What are these fractures

subtrochanteric
greater trochanter #
lesser trochanter #
What does this xray show?

a subcapital #
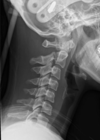
what is a clay shovellers fracture
fracture of the lower cervical vertebrae
c7 and c6
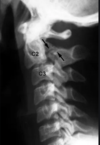
where do mst cervical spine fractures occur?
c2