Renal all Flashcards
(244 cards)
tf kidney is located back of abd cavity
t
kidney regulates blood —
composition
kidneys To balance body water and inorganic ions maintaining stable concentrations in the —– medium
To balance body water and inorganic ions maintaining stable concentrations in the extracellular medium
hematocrit is
rbc / blood vol
tf wbc carry substantial vol
F minimal vol
TF ureter comes from kidney and goes to urethra
F goes to bladder
What are the arows and what do they do
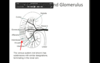
afferent arterioles(perpendicular to interlobular artery)
constrict and dilate
regulate flow of blood
tf aff artioles are innerve by PS innervat
F
Symp innerv.
glomerular filtration happens at
glom. capillaries
tf peritub cap come after the aff arterioles
F
comes after efferent arteriol
which comes in between the 2 arteriole
thick asc. limb
bowmans capsule
thick descendning limb
thick asc limb
number of distal tubules that drain into 1 collecting duct
10
rank the right order
calyx pelvis ureter
pelvis calyx ureter
ureter calyx pelvis
calyx pelvis ureter
TF for filtration to occur u need active transport to occur
F
u dont need anything to facilitate filtration
TF in juxtaglomerular nephron the glomeruli are bigger and loop of henle are longer than cortical nephron
T
granular and lot of dots
cortex with loop of henle
medulla
loop of henle
cortex with glomerular cap
cortex with glomerular cap

afferent arterioles
Vasa recta
exist in cortical nephron
are peritub cap of juxtagom nephron
are convoluted
are peritub cap of juxtagom nephron
arent convoluted
convoluted peritub cap
cotrical nephron
tf macula densa are apart of aff. arteriole
F
part of distal tubule
granular cells are derive from — — cells of the — —
smooth muscle , aff arteriole
in between eff. arteriole aff arterioles and distal tubule
mesangial cells
which of the following is nt a responce to stimulate renin production in the granular cells
composition of fluid going thru distal tubule
pressure in aff arteriole
sympathetic output of kidney
pressur of eff arteriole
pressur of eff arteriole
Na balance and Bp
Renin













