Renal and Urinary Flashcards
(140 cards)
Laboratory Findings of [Post Strep GN] / [Post infectious GN] (4)
- INC ASO (Anti-Streptolysin)
- INC [Anti-DNase B]
- [DEC C3 and total compliment]
- Cryoglobulins
Name the greatest risk factor for [Catheter Associated UTI]
REMOVE CATHETER AS SOON AS IT IS NOT INDICATED ANYMORE
(DURATION IS THE GREATEST RISK)
Most common cause of nephrOtic syndrome in Children and its Tx
A: Minimal Change Dz
B: REVERSIBLE with Corticosteroids
What is almost always associated with Acute Pyelonephritis? (2)
[VUR -Vesicoureteral Reflux] (Anatomical vs. Functional) and [WBC Cast]
Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
A: Clinical Presentation (2)
B: Dx method
C: What’s the earliest sign/detection method for Diabetic Nephropathy
D: Diabetic Nephropathy is the leading cause of _____
A: [Overflow incontinence 2° to inability to sense full bladder] and [incomplete emptying when voiding]
B: [PVR-PostVoid Residual] testing with US vs. Catheter to confirm [incomplete emptying when voiding]
C: [INC Albuminuria ( urine will be)]
D: [ESRD Chronic Kidney Dz]
How does Multiple Sclerosis affect the Bladder?
[Loss of CNS inhibition on [Bladder Detrusor Contraction] allows bladder to always stay contracted –> Urge Incontinence–>eventually progresses [Bladder Atony and Dilation] –> Overflow Incontinence
A: Most common cause of [Nephrolithiasis/Kidney Stones]
B: Most common Risk Factor
C: Other Risk Factors (3)
A: Idiopathic Hypercalciuria = [Normocalcemia + Hypercalcuria]
B: Hypercalcuria
C:
- [Crohn Dz / Fat Malabsorption / Spinach]–> HyperOxaluria
- [Distal RTA Type 1] –> hypOcitraturia
- Gout –> Hyperuricosuria
* Pts are Normocalcemic due to intact serum regulations by Vitamin D and PTH*
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Clinical Manifestation (3)
- [Intermittent Bladder Outlet Obstruction]–>Urinary Retention –> Reflux Nephropathy
- Overflow Incontinence
- Later: Hydronephrosis–>[Renal Interstitial atrophy] –> Chronic Renal Failure
A: How do you Calculate Anion Gap
B: What is the normal Anion Gap
C: Name the Etiologies for [INC Anion Gap Acidosis] (9)
A: Never Carry Hotsauce: [Na+ - (Cl + HCO3)]
B: [10 - 12]
C: “The MUDPILES INC our Gap”
Methanol
Uremia
DKA (Tx= IV normal saline + Insulin)
Paraldehyde
[Isonizid vs. Iron]
Lactic Acid
Ethylene Glycol
Salicylates
DKA- Diabetic KetoAcidosis
A: Tx (3)
C: What type of Anion Gap Acidosis does this cause
D: Why is the pH of the Urine acidic during DKA
A: [IV Normal Saline + Insulin + K+]
C: [INC Anion Gap Acidosis] (MUDPILES)
D: INC production of NH4 & H2PO4
A: Which Renal Structure is subject to Injury from Pelvic Surgery and why?
B: Clinical manifestation (3)
A: Ureters can become unintentially ligated during [Pelvic surgery] –> Obstruction–> [Hydronephrosis w/Flank pain]
B:
- [Flank pain radiating to groin (from ureter and renal pelvis distension]
- [Flank Mass developing within weeks of pelvic surgery]
- [Normal Urine output & Serum creatinine (contralateral kidney compensates)]
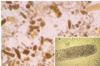
[Post Strep Glomerulonephritis / Post infectious GN]
A: Clinical Presentation (5)
B: Which Kidney is most affectred from PSGN
A: [Older Child/Young Adult] with [Edema / Hematuria (Cola Colored Urine) / ProteinUria] few weeks after [Impetigo vs. pharyngeal infection]
B: Affects BOTH Kidneys (enlarged and swollen)
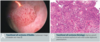
[Pauci Immune ANCA-associated RPGN]
Histology (3)
Is a type 2 Hypersensitivity
1) Absence of Ig and C3 deposit
2) Crescent formation
3) Focal Necrosis
Acute Tubular Necrosis
A: Clinical Course (3 Phases)
B: Outcomes (2)

A:
- Initiation phase =36 hour period = slight DEC in urine output from ischemic/toxic injury
- Maintenance Phase= 1-2 week period= Tubular damage is established –> [Oliguria/Fluid overload/Electrolyte abnormalitities]
- Recovery Phase= [Tubular Re-epithelization] which clears cast –> Transient polyuria and [loss of electrolytes from still impaired tube reabsorption]
B: ([[Renal Function imprvmnt]) vs. [Foci of interstitial scaring –> permanent renal impairment (rare)]

NephrOtic Syndrome
A: Classic Presentation (5)
B: COMMON Renal Complication from this. What are the sx (3)
A: CLag + [Proteinuria > 3.5 gm/day–>FOamy Urine] =
[INC Coagulability from loss of AT3]
[INC Lipidemia]
[DEC alubuminemia] –> Edema
[DEC gammaglobinemia]
B: Renal Vein Thrombosis –>
- Acute Flank Pain
- Hematuria
- [LEFT Varicocele]
A: Describe Histology for Hyaline Arteriolosclerosis
B: Causes (2)
A: [Homogenous deposition of eosinophilic hyaline in intima and media of small vessels]
B:
1) Benign HTN
2) [Diabetic Autonomic NephrOpathy:–> will also have [Kimmelsteil Wilson Nodules from Mesangial Sclerosis]
Where in the Renal Tubule is PAH secreted into?
PCT (but also some PAH is freely filtered by Glomerulus)
so PAH concentration is lowest in Bowman’s Capsule
Describe Tubular Solute Concentrations for Creatinine along the renal tubule (PCT –> Loop–>DCT –> CD)
Basically the same path as [Inulin & Mannitol]
Describe Tubular Solute Concentrations for [Innulin & Mannitol] along the renal tubule (PCT –> Loop–>DCT –> CD)
Basically the same path as Creatinine
FORMULA for:
A: RPF: Renal plasma Flow
B: RBF: Renal Blood Flow. - Also Define RBF
C: Filtration Fraction
A: rpf = PAH Clearance =UV / P
B: RBloodF = [rpf ÷ (1 - Hct)] = volume of blood flowing thorugh kidneys per unit time
C: [Filtration Fraction] = [GFR ÷ rpf]
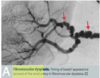
A: Demographic for Renal Artery Stenosis (2)
B: Manifestations (3)
A:
- Elderly
- [Pregnant Women 2º to fibromuscular Dysplasia]
B:
- Unilateral Kidney Atrophy
- HTN
- Abd Bruit
- R Kidney Atrophy from RAS in image*
Promoters of Nephrolithiasis (8)
IM COUGHS
- Injury
- [Mg+ –> Struvite Stones]
- Calcinuria**
- Oxalate INC**
- [Uric Acid INC in urine (Tumor lysis syndrome vs. Gout)
- Gravity
- Hydrogen ions
- Sodium
A: INHIBITORS of Nephrolithiasis (2)
B: Once a pt develops Nephrolithiasis, what are the tx (4)
- CITRATE (found in Fruits & Veggies) + Hydration
- INC Urine Flow
B:
- Tamsulosin
- NSAIDs
- [INC Fluid Intake to 2-3 L/day]
- Proximal Ureter location –> Surgery
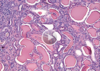
A: Describe Histology for [Multiple Myeloma Nephropathy]
B: Demographic
C: Other common sx with this presentation (3)
A: [Large Eosinophilic light chain cast] made of [Bence Jones proteins] in tubular lumen –> [1º DTiN-DrugTubularInterstitialNephritis]
B: Elderly