Renal Path (Holanda) Flashcards
(42 cards)
What are the characteristics of the following three main clinical renal syndromes?
acute kidney injury: ________
nephrotic syndrome: _______
nephritic syndrome: ________
acute kidney injury: oliguria (low urine output) and rapid rise in serum creatinine
nephrotic syndrome: severe proteinuria
nephritic syndrome: hematuria
(She stressed this is an important slide to know)
where does acute kidney injury most commonly occur?
in the proximal tubule
what is the defect that is associated with nephrotic syndrome?
glomerular capillary filtration defect (usually in the podocyte side of the urinary space)
what is the injury most commonly associated with nephritic syndrome?
it is usually due to breaks in the glomerular capillary loops, causing red cells to spill out into the urinary space
what two lab values would indicate an acute kidney injury?
serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
glomerular sclerosis, interstitial fibrosis, and tubular atrophy are all common findings in ____ kidney disease
chronic

which of the following statements regarding immunofluorescence staining in the glomerulus is FALSE?
A. Renal biopsy is routinely stained for IgM, IgA and IgG
B. Mesangial pattern is indicative of IgA nephropathy
C. A granular capillary loop pattern indicates membranous nephropathy
D. immunofluorsecence stains for some complement proteins and the kappa/lambda light chains
E. A linear capillary loop pattern indicates lupus nephritis
E. Linear capillary loop patterning is indicative of Anti-GBM disease. Mesangial and Granular patterns may be indicative of lupus or IgA nephropathy (see below).

mechanisms of this type of kidney disease include immune complex mediated, t-cell mediated, and genetic structural disorders (ie, Alport’s syndrome)
glomerular
syndrome that results from a defect in the collagen type IV gene, which causes structural weakness to the glomerular basement membrane
Alport’s syndrome
All of the following are true of acute tubular necrosis EXCEPT:
A. It is the most common cause of acute kidney injury
B. It is often caused by hypovolemia, ischemia or drug toxicity
C. It is usually irreversible
D. Caused by injury to tubular epithelial cell
E. Characterized by acute onset of kidney injury with development of oliguria
C. On the contrary, acute tubular necrosis is often reversible.
a key feature of this disease is evidenced by eosinophilic granules in the cytoplasm, as shown below:

acute interstitial nephritis; commonly caused by drugs
key findings in this disease are tubular dilation with necrotic debris, and flattening of tubular epithelial cells, as shown below:

acute tubular necrosis
key physical findings in this disease include signs of infection and histological/gross findings show abscesses of neutrophilic infiltrates (see below); symptoms often are abated with antibiotic treatment
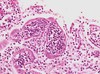
Acute pyelonephritis; very similar in appearance to acute interstitial nephritis but the inflammatory infiltrates include many more neutrophils
dilated atrophic tubular cells filed with hyaline casts, surrounded by swaths of fibrotic tissue is characteristic of what chronic disease?
chronic pyelonephritis; cells resemble thyroid
A 55 year old woman was involved in a car accident. She was in hypovolemic shock due to loss of blood.
She has reduced urinary output in the ICU.
Her serum creatinine was 3.5mg/dL( Normal < 1.0mg/dL)
Urine microscopic examination – normal ( no red cells, no proteinuria)
What clinical renal syndrome does she have?
acute tubular necrosis
In a patient with acute tubular necrosis, what changes would a biopsy show?
A. Interstitial inflammation with eosinophils
B. Dilated tubules with necrotic material
C. Hypercellular glomeruli
D. Interstitial inflammation with numerous neutrophils
B
features of this disease include dark colored urine due to erythrocytes, and may be accompanied by acute kidney injury, as indicated by serum creatinine and BUN
(acute) nephritic syndrome
this is the most common type of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide, which particularly affects African American young adults and is characterized by recurrent hematuria
IgA nephropathy; H&E shows mesangial proliferation (>3 cells in each mesangial region, see below)

_____ is a clinical sign that indicates progressive IgA disease, and may call for steroids or other immunosuppressives (varying success rate)
proteinuria
this disease is a vasculitic variant of IgA nephropathy usually seen in children, and features arthritis, abdominal pain and rashes
Henoch Schonlein purpura (HSP)
rare disease that is most often inherited in an x-linked dominant pattern and presents with sensorineural deafness and microscopic hematuria
Alport’s syndrome; microscopy of this would show variability in the thickness of the glomerular basement membranes (see below). Also characteristic is a “basket weave” pattern of the membrane.

what 2 conditions cause acute nephritic syndrome?
crescentic glomerulonephritis and diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
This type of glomerulonephritis shown below is illustrated by the compression and breaking of capillary loops (black stained) and the leaking of fibrotic material into the Bowman’s space:

crescentic glomerulonephritis; she stressed that crescentic GN always implies vasculitis.
disease that is the type I subcategory of crescentic glomerulonephritis, characterized by abnormal production of antibodies against collagen type IV in the GBM
Goodpasture’s disease (anti-GBM disease); as with all crescentic GN diseases, you treat this with high dose steroids, toxic agents and plasmapheresis








