Renal Pathophysiology Flashcards
(235 cards)
How is GFR measured?
clearance of inulin or creatinine
estimates based on serum creatinine
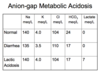
azotemia
accumulation of nitrogenous waste products in the blood
i.e. urea
any rise in serum BUN or creatinine above normal
uremia
clinical syndrome or symptom compelx associated with severe impariment of renal function
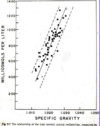
specific gravity of urine
lower specific gravity correlated with low osmolarity (more dilute urine)

This is an example of a urine
1: Here a white cell with red blood cells around it
When you see cells in the urine you do not know if they have come from the kidney or someplace else in the urinary tract a

WBCs and bacteria in urine

tubular epithelial cell (not round like WBC)

squamous epithelial cells - from bladder ureter or urethra NOT kidney
casts
cylindrical masses of agglutinated material
formed in distal nephron, have to come from kidney
Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein is the major protein constituent
Hyaline, granular or cellular
Where are casts formed?
distal nephron
Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein
major protein constituent of casts
Hyaline cast
we think the hyaline cast and granular cast are degenerated cellular casts
There is a lot of other amorphous material here

tubular epithelial cell cast
you can see the shape of the cells here are not perfectly round which you would see in a white blood cell cast

broad cast
it was formed further down in the nephron, again there are red cells around this cast

coarse granular cast
notice the granules and degenerating cells

RBC cast

WBC cast

waxy cast (probably has cholesterol)

triple phosphate crystals
often in people with UTIs

calcium oxalate crystals

On the left there are stellar and amorphous Ca Phosphate crystals
On the right Ca Oxalate crystals

cysteine crystals

uric acid crystals
What does dipstick look for?
•Dipsticks (mainly picks up albumin, may miss low molecular weight and other nonalbumin proteins)