Respiration Flashcards
(142 cards)
the components of the respiratory system
- Respiratory Tract Thorax: Thoracic wall and thoracic cavity
the major function of the respiratory tract (and other functions)
- Major function: Air distribution (all parts except alveoli), Gaseous exchange (alveoli) 2. Other Functions: Filters, Warms and humidifies the air, Resonance of voice, Regulation of CO2-O2 levels in the body, Smell
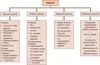
Gross anatomy of the respiratory tract
Subdivisions of Respiratory Tract: Upper respiratory tract: Components outside the thorax: 1. Nose 2. Paranasal sinuses 3. Pharynx: Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx 4. Larynx Lower Respiratory Tract: Components located almost entirely within the thorax 1. Bronchial tree Lungs
Nose (Ala)
each side of the nostril
Nose (Nasal septum)
divides nose into left and right cavities
Nose (Turbinates)
bony projections on the lateral wall of nasal cavity (superior, middle, inferior- has rich blood supply)
Nose (anterior nares)
external openings of nose
Nose (posterior nares)
openings into pharynx; allows air to pass from nose to pharynx
Vestibule
area just inside the nasal cavity- contains vibrissae (hairs), glands
Nasal muscosa components
- Respiratory mucosa Olfactory mucosa: special sensory for smell.
Define paranasal sinuses
hollow spaces in skull bones and facial bones; all of these are connected to the nasal cavity
4 pairs of paranasal sinuses
Frontal, Maxillary, Ethmoid, Sphenoid
Functions of paranasal sinuses
- Airway passageway 2. Warms, moistens, filters air Sinuses, provide resonance for voice
define Pharynx
muscular tube, lined with mucous membrane extending from base of skull to esophagus
3 subdivisions of the pharynx
- Nasopharynx: from posterior nares to soft palate 2. Oropharynx: from soft palate to hyoid bone in neck 3. Laryngopharynx: from hyoid bone to esophagus
function of the pharynx
Common passageway for respiratory and digestive tracts, Role in speech (laryngopharynx)
define Larynx
Voice box: Lies between root of tongue and upper end of trachea.
Location of the larynx
against bodies of cervical vertebrae 3 to 6 (related to thyroid gland).
functions of the Larynx
Air passageway, Voice production, Protects airway against entrance of solids or liquids.
Organisation of the larynx
• Cartilage framework • Held by muscles and ligaments • Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles Contains: true vocal cords (Glottis) and rima glottidis
Trachea
• Windpipe • Extends from larynx to principal bronchi: 2.5cm in diameter, 15-20 C-shaped rings- hyaline cartilage, posterior surface (trachealis) • Lines by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
the two functional subdivisions of the respiratory tract
- Conducting Zone: passageways for air: nasal cavity to terminal bronchioles 2. Respiratory Zone: gaseous exchange: respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs and alveoli
components of the thoracic wall and thoracic cavity
- Ribs and Rib cage 2. Joints- ribs with sternum, ribs with vertebrae 3. Phases- events of respiration 4. Alteration in capacity of thorax Movements of ribs and mechanics of rib movements
what are the factors facilitating changes in the diameter
oints of sternum, joints at vertebral column, obliquity of ribs