Rheum Flashcards
(424 cards)
two specific circumstances where methotrexate is commonly used
RA, its usualyl a first line drug
SLE when there is significant arthritis
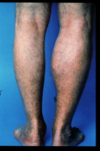
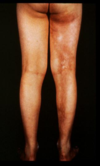
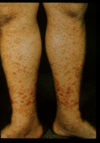
Systemic lupus erythematosus description
an inflammatory autoimmune disease typically affecting women caused by antinuclear antibodies that leads to trapped antigen complexes in blood vessels
SLE therapy
NSAID
depends on symptms
NSAIDs for joint pain
hydroxychloroquine for joint pain, rash, fatigue
steroids for arthritis, serositis, major organ involvement
methotrextate for arthritis
leflunomide arthritis, rash, major organ involvement
angiogram findings with polyarteriris
multiple anuerysms with tapered narrow and skip areas
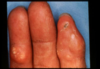
diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis
Elevated ESR
normochromic, normocytic anemia
hyperuricemia with significant skin involvement
normal rheumatoid factor
pencil cup deformitity at the PIP on xray
SLE therapy
steroids
steroids for arthritis, serositis, major organ involvement
fibrocartiliaginous joints
synarthrosis with limited movement
ankylosing spondylitis clinical presentation
limited ROM in the lumbar spine, hips, shoulder
synovitis in the knees, achilles, plantar fascia
up to 25% will have anterior uveitis
pain and stiffness that lasts for hours and is made better with activity

uveitis
what is this and what causes it

chondrocalcinosis
gout or arthritis
Dx of fibromyalgia
clinical presentation
exclusion of other factors (hypothyroid, hep c, vitamind D deficiency)
PE findgs for psoriatic arthritis
dactlyitis
enthesitis
skin lesions
nail dystrophy/pitting
sacroilitis
why are eye or pulmonary involvement or vasculitis common in RA
b ecause RA is an inflammatory systemic disease
top three treatment for myositis
steroids
methotrexate
azathioprine
management of OA
medication, rest, exercise, diet, surgery, aids
biologics defined for RA
genetically engineered molecules that work on specific targets
splinter hemorrhages
cause
vertical hemorrhages under the nails
can be caused by vasculitis or bacterial endocarditis
GI protective strategies for NSAIDs
cox 2 nsaid
nsaid with PPI
nsaid with misprostol
nsaid with H2 blocker
radiographic findings associated with OA
narrowed joint space, osteophytes, subarticular cysts
proteoglycans
glucosamine and chondriotin
Dx of giant cell arteritis
elevated ESR and CRP
most patients will have normochromic normocytic anemia with thrombocytosis
temporal artery biopsy that shows thickening
patient presents with a gout flare up and they are curently not on allopurinol
should you start it?
what if they are in a flare up and on allopurinol
no, don’t start it during an acute flaire
no, don’t stop it during a flare if you are already on it
Rhabdomyolysis
a syndrome of acute necrosis of skeletal muscle indicated by myoglobinuria and elevated creatine kinase
T/F the risk of CVD in patients with RA is the same as with diabetes
treu