S10) Anxiety Disorders Flashcards
(61 cards)
Why is the stress response important?
causes a feeling of anxiety to enable us to escape from potentially dangerous situations.
What is the stress response to allow us to get away from threat mediated by?
- limbic system (neural elements of the stress response)
- limbic-hypothalamo-pituitary- adrenal axis (endocrine elements of the stress response where the limbic system is able to act on the hypothalamus to stimulate secretion of stress hormones)
What is the limbic system?
- The limbic system is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the cerebrum
- It supports a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction
Identify the components of the limbic system
- Hippocampal formation
- Septal area
- Amygdala
- ± Prefrontal cortex
- ± Cingulate gyrus

Briefly outline the functioning of the limbic system
Hypothalamus - key organ related to stress response - releases CRH - corticotropin releasing hormone - key -links to SNS activation and wider effects via cortisol release.

Describe the structure of the hippocampus.
– Curved piece of cortex
– Folded into medial surface of temporal lobe
– Occupies floor of temporal horn of lateral ventricle
– Three parts: subiculum, hippocampus proper, dentate gyrus

What is the function of the hippocampus?
Involved in memory and expressions of emotion
Describe the inputs and outputs of the hippocampus.
Describe what it leads to.
Inputs from: many parts of the cortex and processes their emotional content
Output: to the thalamus (and hence back to the cortex – the Papez circuit) and also to the hypothalamus (causing autonomic features of emotional responses, since the hypothalamus send projections down through the cord to autonomic preganglionic neurones – the hypothalamospinal tract.
This will lead to sympathetic nervous system activation, as well as release of adrenaline from the adrenal medulla – the acute stress response)
o Role in memory – already discussed
→ Papez circuit may be involved in memory consolidation
Describe the structure of the amygdala?
– Almond shaped structure sitting near the tip of the hippocampus
– Buried in the roof of lateral ventricle
– Collection of nuclei

What are the inputs and outputs of amygdala?
Inputs of sensory information, brainstem, thalamus, cortex
Outputs to cortex, brainstem and hypothalamus
What is the function of the amygdala?
Drive related behaviours and processing of associated emotions
Like the hippocampus, it is involved in behavioural and autonomic emotional responses
What is the function of the prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate gyrus?
Both have modulatory effect on processes associated with the hypothalamus
Prefrontal cortex (classically not part of the limbic system but definite roles in emotion)
o Modulation of emotional responses (e.g. consciously suppressing features of anxiety)
o ‘Perception’ of emotion?

Briefly outline the limbic-hypothalamo- pituitary-adrenal axis

In the activation of a stress response, what does the SNS activation result in?
Increased heart rate and force of contraction
Dilated bronchi

Endocrine elements of the stress response
• The limbic system is able to act on the hypothalamus to stimulate the secretion of stress hormones via the familiar hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis
Describe the HPA axis.
Release of cortisol from the adrenal cortex is part of
the ‘chronic’ stress response

What are the actions of cortisol?
- Increase of energy metabolite levels
- Suppression of immune system
- Inhibition of allergic and inflammatory processes

Describe the fight or flight response.

What is the general adaptation syndrome referring to?
The general adaptation syndrome refers to three stages that the body goes through
during prolonged exposure to stressors
What are the three components of the general adaptation syndrome?
Stage 1 - the alarm reaction
Stage 2 - Resistance (effect of adrenaline starts to wear off)
Stage 3 - Exhaustion (when you cannot escape an ongoing stressor)

Which three process occur in the alarm reaction part of general adaptation syndrome?

- NA release from sympathetic nerves
- Adrenaline and NA release from adrenal medulla
- Cortisol release from adrenal cortex
(Release of adrenaline and cortisol as well as sympathetic activation)
What occurs in the resistance part of general adaption syndrome?

Resistance – action of cortisol is longer lasting than adrenaline, allows maintenance of response to stress
Resistance (effect of adrenaline starts to wear off)
Chronic stress response, prolonged release of cortisol
What occurs in the exhaustion part of general adaptation syndrome?

Exhaustion – prolonged stress causes continued cortisol secretion, leading to muscle wastage, suppression of immune system and hyperglycaemia
(when you cannot escape an ongoing stressor)
Chronic side effects of prolonged cortisol secretion start to occur
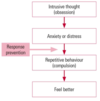
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a feeling of worry, nervousness or unease about something with an uncertain outcome
Anxiety is the term used for a pathological stress response
Why do we get anxious?

– part of normal/ necessary thing esp with linkage to threat
– has an evolutionary process, makes us safer?
need to be anxious to get away from a threat