S1B5 - Autonomic Physiology 1 Flashcards
(42 cards)
Each connection or pathway in the autonomic nervous system is composed of how many fibers?
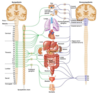
The connections or pathways of the autonomic nervous system are composed of two fibers, a preganglionic and postganglionic fiber.
What division of the autonomic nervous system can function independent of the central nervous system?
The enteric nervous system functions via a system of intramural ganglia and plexuses that can function independently of the central nervous system. Please note that the majority of the time, there is input from the central nervous system via the autonomic nervous system.
Where do preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system originate from?
Preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system originate in the intermediolateral cell column (T1-L2) of the spinal cord.

Are postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system short or long?
Postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system are long.

What is the predominant neurotransmitter of postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system release acetylcholine (ACh).

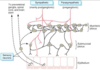
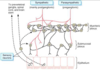
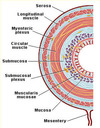
What innervation does the myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus carry and to what layer of the gastrointestinal wall?
Two nerve plexuses within the gut coordinate gastrointestinal motility and secretions, respectively:
- Myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus: provides sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation to the muscularis propria to coordinate motility
- Submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus: provides parasympathetic (secretomotor) innervation to the mucosa and muscularis mucosae to coordinate secretory function
Are the preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system short or long?
Preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system are short.

What is the predominant receptor type on target organs of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Target organs of the parasympathetic nervous system have muscarinic receptors (M1, M2, etc.).

What is the major neurotransmitter of the enteric nervous system?
The major neurotransmitter of the enteric nervous system is serotonin (5-HT), which generally promotes motility.

What is the only organ that is directly innervated by preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system?
There is one component of the sympathetic nervous system that does not follow the two neuron rule. Some preganglionic neurons directly innervate the adrenal medulla, which then releases epinephrine into the general circulation.
What is the primary function of the enteric nervous system?
The enteric nervous system primarily serves to regulate gastrointestinal motility.

What is the role of sensory neurons in the enteric nervous system?
Sensory neurons in the intestinal mucosa and muscularis propria layers sense acid, glucose, amino acids, osmotic changes, muscle stretch, and muscle tension. This information is relayed back to the central nervous system so that it can coordinate proper autonomic output to the enteric nervous system.
What is the general function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
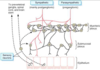
The parasympathetic nervous system is generally involved in “rest and digest” responses such as decreasing heart rate, bronchoconstriction, and increasing blood flow to the GI tract.

What body system regulates visceral functions?
The autonomic nervous system serves to regulate visceral functions, including smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glandular tissue.
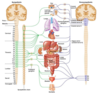
Where do preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system originate from?
Preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system originate in the cranial and sacral regions of the CNS including:
- CNs III, VII, IX, and X
- S2, S3, S4

What neurotransmitters are released by postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system that innervate sweat glands and renal blood vessels?
Two exceptions are postganglionic neurons that innervate sweat glands, which release acetylcholine (ACh), and postganglionic neurons that innervate renal blood vessels, which release dopamine.

Where (2 locations) do postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system originate?
Postganglionic neurons originate in two locations, each with distinct targets which include:
- Sympathetic trunk, projecting to blood vessels, sweat glands, and arrector pili muscles
- Prevertebral ganglia, projecting to abdominal and pelvic viscera
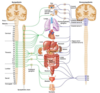
What division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the “fight or flight” response?
The sympathetic nervous system is generally involved in “fight or flight” responses. Its activity results in various changes including increased heart rate, bronchodilation, and increased blood flow to skeletal muscles.

Are postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system long or short?
Postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system are short.

Are preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system long or short?
Preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system are long.

What target of the sympathetic nervous system has muscarinic acetylcholine receptors?
Sweat glands have muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. This is important because muscarinic antagonists, such as atropine that act specifically on M3 receptors, can affect the sweat glands.

What type of receptor is found at the synapse between the preganglionic and postganglionic neurons in both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
For both the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, the receptor type at the synapse between the preganglionic and postganglionic neurons (including between the preganglionic neuron and adrenal medulla) is a nicotinic cholinergic receptor.

Which gastrointestinal nerve plexus provides only parasympathetic innervation to the mucosa and muscularis mucosae?
Two nerve plexuses within the gut coordinate gastrointestinal motility and secretions, respectively:
- Myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus: provides sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation to the muscularis propria to coordinate motility
- Submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus: provides parasympathetic (secretomotor) innervation to the mucosa and muscularis mucosae to coordinate secretory function
What is the predominant receptor type on target organs of the sympathetic nervous system?
Target organs of the sympathetic nervous system, except the sweat glands and renal vessels, have adrenergic receptors.