S7) The Nervous System Flashcards
(21 cards)
Describe the basic layout of the nervous system

Which nerve roots do the sensory and motor neurons accompany?
- Sensory neuron accompanies dorsal nerve root
- Motor neuron accompanies ventral nerve root

What are fascicles?
Fascicles are bundles of nerve fibres

Describe the arrangement of connective tissues in the nerves of the body
- Groups of fascicles are held together by the epineurium
- Individual fascicles are surrounded by the perineurium
- Individual nerve fibres are surrounded bu the endoneurium

What are the two types of cells in the nervous system?
- Neurones
- Glial cells
Identify the 2 types of glial cells in the body
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells

Distinguish between a Schwann cell and an oligodendrocyte in terms of myelination and location
- Oligodendrocytes can myelinate many axons and are found in the CNS
- Schwann cells can only myelinate one axon and are found in the PNS

What do astrocytes do?
- Extend processes out towards synapses and ‘ vacuum ‘ up any excess neurotransmitters
- Produce changes in the brain cells to create a blood/brain barrier, preventing toxins/bacteria/pathogens getting from the blood to the brain
What are microglia cells ?
Microglia cells are mobile immune cells of the CNS

What do microglia cells do?
- Microglia cells have constantly moving processes that are constantly looking for pathogens and antigens
- When found they will develop into macrophages

Where are the autonomic preganglionic neurone cell bodies found in the CNS?
Sympathetic – lateral horn in T1-L2 cord segments
Parasympathetic – S2-S4 cord segments and brainstem
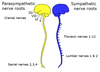
Describe the 4 different ways preganglionic fibres of the sympathetic nervous system can be distributed
- Ascend the chain then synapse (typically to supply the head and neck)
- Synapse at the level of entry (to supply dermatomes at the T1-L2 levels)
- Traverse the chain then synapse in a pre-aortic ganglion (to supply abdominal viscera)
- Descend the chain then synapse (typically to supply the lower limbs)
Describe the 2 different ways postganglionic fibres of the sympathetic nervous system reach their targets
- Postganglionics reach their targets along the walls of blood vessels
- Postganglionics reach their targets along spinal nerves
What is the major source of parasympathetic preganglionic input to the thoracic and abdominal viscera?
Vagus nerve
The head has 4 specialised parasympathetic ganglia. Identify them
- Ciliary ganglion
- Pterygopalatine ganglion
- Submandibular ganglion
- Otic ganglion

Describe the function of the ciliary ganglion
The ciliary ganglion receives parasympathetic preganglionics from the oculomotor nerve and distributes parasympathetic postganglionics to the eye

Describe the function of the pterygopalatine ganglion
The pterygopalatine ganglion receives parasympathetic preganglionics from the facial nerve and distributes parasympathetic postganglionics to the lacrimal gland
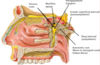
Describe the function of the submandibular ganglion
The submandibular ganglion receives parasympathetic preganglionics from the facial nerve and distributes parasympathetic postganglionics to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands

Describe the function of the otic ganglion
The otic ganglion receives parasympathetic preganglionics from the glossopharyngeal nerve and distributes parasympathetic postganglionics to the parotid gland

What is referred pain?
Referred pain is where a pain is perceived at a site distant to the source of the pain
Distinguish between visceral and somatic pain
Somatic pain comes from the joints, bones, muscles and other soft tissues, while visceral pain comes from the internal organs


