Scavenging systems and CO2 absorbers Flashcards
(91 cards)
What is the purpose of the scavenging system?
To collect excess gases from anesthesia equipment or exhaled by patients and remove them to an appropriate place outside the work envirnoment
The scavenging system has the added benefit of removing __________ from the machine and preventing build up.
pressure, especially where high flows are used
What is NIOSH?
National Institute of Safety and Health; they set the recommendations for anesthetic gas levels in the OR.
How much volatile anesthetic gas alone is permitted in the OR according to NIOSH?
**2ppm ** (note:without nitrous you can tolerate more volatile anesthetic in the envirnoment, with nitrous is it is much less)
How much nitrous oxide is permitted in the OR according to NIOSH?
25 ppm
If you have both volatile anesthetic and nitrous, how much does NIOSH permit in the OR?
0.5 ppm
Name some things that might increase or decrease the amount of anesthetic gas in the OR?
Delivering anesthesia by mask, taking mask on and off, increases anesthetic in the air. But, because the air in the OR is turned over about 20x an hour, the anesthetic is quickly diluted out. Scavenging of gases also limits our exposure. Care providers can experience symptoms of the anesthetic when exposed, and miscarriage, liver damage, neurological symptoms and other adverse events in the provider have occurred.
The scavenger system alarm will alert you when the system is malfunctioning, (T or F)
F. There is not alarm on the scavenging system. This must be checked with your daily machine check.
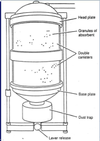
What is this?

This picture shows a basic scavenging system using a reservoir bag.
What are the 5 basic components of the scavenging system?
Gas collecting assembly, transfer means, scavenging interface, gas disposal tubing, gas disposal assembly
Label the 5 components of the scavenging system


Describe the gas collecting assembly portion of the scavenging system.
It captures excess gases at the site of emission. From the APL valve if manually ventilating or from the Ventilator relief valve (excess gas from the vent/ driving gas can be part of this). They are then delivered to the transfer means tubing.
What size are the connections in the gas collecting assembly of the scavenging system and why is their size important?
The outlet connection is 30mm (19 mm in older machines) (male-fitting). It is important to to have connection sizes that are incompatible with any other part of the breathing system to prevent an accidental misconnection of lines.
Describe the transfer means portion of the scavenging system.

Also called exhaust tubing or hose and transfer system. It conveys gas from the collecting assembly to the interface. It us usually a tube with female fitting connectors on both ends. The tubing is short with a wide diameter to carry a high flow of gas w/o a significant increase in pressure. It must be kink resistant. It must be different from breathing tubes. (usually stiffer and colored yellow)
The scavenging interface prevents ___________ changes from being transferred to the breathing system.
pressure
The scavenging interface is also called the?
balancing valve or device
The scavenging interface limits pressures immediately downstream of the gas collecting assembly to between:
-0.5 to +5 cmH2O
The scavenging interface inlet should be what size?
30mm male connector
The scavening interface should be positioned where?
as close to the gas collecting assembly as possible.
What are the 3 basic elements of the scavenging interface?
- positive pressure relief protects patient and equipment in case of occlusion of system -negative pressure relief-limit subatmospheric pressure -reservoir capacity matches the intermittent gas flow from gas collecting assembly to the continuous flow of disposal system
The scavenging interface comes in two types, they are:

Open or Closed
Does the open interface have valves?
No. It is open to the atomosphere via holes in the reservoir, avoiding buildup of positive or negative pressure. If pressure builds up, pressure will be released out via the holes, if vacuum is powerful, the reservoir will not crush/ collapse, it will pull air through the holes in to relieve pressure
Does the open interface require a vacuum?
Yes, it requires a central vacuum and a reservoir that is an open cansiter, large enough to accomodate high waste gas flows. (Envision a metal coke can- gases sit in the reservoir until they can be sucked away by the vacuum. When the vacuum is on, the canister does not collapse, it pulls atmospheric air into it via the holes and flushes the anesthetic gases through) Make sure there are no surgical drapes, or other things blocking the relief holes.
How much vacuum pressure should be on in an open interface?
It can be adjusted. It must be higher than the excess gas flow, otherwise you will get spill out through the relief holes into the OR atmosphere.