Science Flashcards
(133 cards)
Gland/Organ: THYROID GLAND Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: THYROID GLAND Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Triiodothyronine T3 Function: Metabolism
- Hormone: Thyroxin T4 Function: Metabolism and temperature
- Hormone: Calcitonin Function: Inhibits release of Calcium from bones

Gland/Organ: ADRENAL MEDULLA Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: ADRENAL MEDULLA Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Epinephrine Function: fight
- Hormone: Norepinephrine Function: flight

Gland/Organ: Kindneys Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Kindneys Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Etyhropoietin Function: Response to cellular hypoxia
- Hormone: Renin Function: Promotes production of Angiotensin

Gland/Organ: Thymus Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Thymus Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: Thymosin Function: Stimulates T-Cell

Gland/Organ: Adrenal Cortex Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
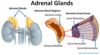
Gland/Organ: Adrenal Cortex Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Cortisol/Glucocorticoids Function: Increase blood glucose, Stress response, metabolism, Decrease immune response;
- Hormone: Aldosterone Function: Regulates Na content in blood

Gland/Organ: Pineal Gland Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Pineal Gland Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Melatonin Function: Sleep cycles; biorhythms

Gland/Organ: Ovaries (female gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Ovaries (female gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Estrogen Function: Stimulates egg maturation, controls 2ndary sex characteristics
- Hormone: Progesterone Function: Prepares uterus to receive fertilized egg

Gland/Organ: Parathyroid Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Parathyroid Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Function: Stimulates release of calcium from bones, back into blood.

Gland/Organ: Intestine Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Intestine Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Secretin Function: Response to acidity in small intestine; stimulates secretion by liver and pancreas
- Hormone: Cholecystokinin Function: Production of Bile Salts
Gland/Organ: Heart Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Heart Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) Function: Increase renal Na excretion, decrease ECF

Gland/Organ: Testes (male gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: LIVER Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Angiotensin II Function: Vasoconstriction, Increase BP

Gland/Organ: STOMACH Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: STOMACH Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Gastrin Function: Response to food;stimulates production of gastric juice

Gland/Organ: Hypothalamus Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Hypothalamus Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: ___________________
- Hormone: Releasing/Inhibiting hormones Function: Stimulate Pituitary

Gland/Organ: Anterior Pituitary Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Anterior Pituitary Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Function: Stimulate adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids
- Hormone: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Function: Stimulate the Thyroid gland
- Hormone: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Function: Stimulates production of ova (females) and sperm (males)
- Hormone: Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Function: Stimulates Ovaries (females) and Testes (males)
- Hormone: Prolactin Function: stimulates milk production
- Hormone: Growth Hormone (GH) Function: Stimulates growth (bones) and metabolic functions

Gland/Organ:Posterior Pituitary (back) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ:Posterior Pituitary (back) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: (ADH) Antidiuretic Hormone/ Vasopressin Function: Promotes retention of water by the kidneys
- Hormone: Oxytocin Function: Stimulates contraction of uterus and mammary gland cells

Gland/Organ: Pancreas Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: (Alpha Cells)_____________Function: _______________
- Hormone: (Beta Cells)______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Pancreas Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: (Alpha Cells)_____________Function: _______________
- Hormone: (Beta Cells)______________ Function: _______________
Gland/Organ: Pancreas Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: (Alpha Cells) Glucagon Function: Increase blood glucose
- Hormone: (Beta Cells) Insulin Function: Decrease blood glucose

Gland/Organ: Testes (Male Gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: _____________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Testes (make gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: _____________Function: _______________
Gland/Organ: Testes (make gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: Testosterone Function: Regulates sperm production and 2ndary sex characteristics

Which of the following describes cellular respiration?
It is a reductive catabolic activity
It is an oxidative anabolic activity
It is an oxidative catabolic activity
It is a reductive anabolic activity
Answer: It is an oxidative catabolic activity
Which of the following describes cellular respiration?
It is a reductive catabolic activity
It is an oxidative anabolic activity
It is an oxidative catabolic activity
It is a reductive anabolic activity
An anabolic reaction is a reaction that uses energy to build molecules the organism needs. A catabolic reaction breaks down complex molecules into smaller molecules to create energy for the organism to use.
Oxidation is when an element loses one or more electrons to oxygen. Reduction is when an element gains one or more electrons.
Cellular respiration is the process in which a cell takes in oxygen and uses it to break down glucose to create energy in the form of ATP. In the final stage of cellular respiration (called the electron transport chain), oxygen accepts electrons and picks up protons to form water. So, because elements lose electrons to oxygen and it is a reaction in which energy is created, cellular respiration is both an oxidative and catabolic activity.
Which of the following types of tissues functions in the covering, lining, and protection of surfaces and body cavities?
Epithelial tissue
Connective tissue
Muscle tissue
Nerve tissue
Answer: Epithelial tissue
Which of the following types of tissues functions in the covering, lining, and protection of surfaces and body cavities?
Epithelial tissue
Connective tissue
Muscle tissue
Nerve tissue
Epithelial tissue functions as the lining and covering of body surfaces and cavities.
Muscle tissue functions in facilitating voluntary and involuntary movements.
Connective tissue is responsible for the support and protection of tissues and organs.
Nerve tissue is responsible for transmitting nerve impulses.
The respiratory system is composed of organs that facilitate gas exchange between the blood and the external environment. Which of the following describes the group of organs that function during ga exchange?
Organ
Organelle
Organ System
Tissue
Answer: Organ system
The respiratory system is composed of organs that facilitate gas exchange between the blood and the external environment. Which of the following describes the group of organs that function during ga exchange?
Organ
Organelle
Organ System
Tissue
Tissues are a collection of specialized cells that perform a specific functions (e.g. protection, support, nerve conduction and movement).
A group of tissues that has a specialized function is referred to as an organ.
A group of organs that work together to perform several related functions is an organ system.
Below is a model representing the hierarchy of the structure of the human body:

White blood cells contain many _________ because they need to dispose of harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. Which of the following options correctly completes the statement above?
ribosomes
lysosomes
mitochondria
Golgi
Answer: lysosomes
White blood cells contain many _________ because they need to dispose of harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. Which of the following options correctly completes the statement above?
ribosomes
lysosomes
mitochondria
Golgi
White blood cells contain a larger number of lysosomes because they need to dispose of harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. Lysosomes are responsible for digesting and removing waste from a cell. This means they can digest bacteria and viruses that are engulfed by white blood cells in order to protect the body.
Mitochondria are the organelles responsible for generating energy-rich molecules for the cell.
The Golgi apparatus collects small molecules and combines them to make more complex molecules within the cell. Then it packages up the complex molecules to either store or to send out of the cell.
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. mRNA is translated into proteins by the ribosomes.
Which of the following organ systems is correctly paired with its function?
Digestive/ waste elimination
Endocrine/ regulation of homeostasis through hormone signaling
Circulatory/ obtaining nutrients necessary for growth, energy and normal body processes
Excretory/ transport of substance to all tissues of the body
Answer: Endocrine/ regulation of homeostasis through hormone signaling
Which of the following organ systems is correctly paired with its function?
Digestive/ waste elimination
Endocrine/ regulation of homeostasis through hormone signaling
Circulatory/ obtaining nutrients necessary for growth, energy and normal body processes
Excretory/ transport of substance to all tissues of the body
The Endocrine system is responsible for regulating homeostasis through hormone signaling.
The Digestive system is responsible for obtaining nutrients through the breakdown and absorption of food.
The Circulatory system is responsible for transport of substance to all tissues of the body.
The Excretory system is primarily responsible for waste elimination.
Which of the following correctly describes anatomical position?
Upright, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Seated, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Supine, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Prone, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Answer: Upright, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Which of the following correctly describes anatomical position?
Upright, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Seated, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Supine, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Prone, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Anatomical position is described as standing erect, arms at sides, face and palms are facing anteriorly (facing to the front).

HIV is a virus that destroys the body’s defense against diseases by inserting itself into the host’s DNA. In which part of the infected host cell will HIV virus be found?
Ribosomes
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Nucleus
Answer: Nucleus
HIV is a virus that destroys the body’s defense against diseases by inserting itself into the host’s DNA. In which part of the infected host cell will HIV virus be found?
Ribosomes
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Nucleus
HIV infects a host cell by integrating its genetic material with the genetic material of the host cell. Genetic material is located in the nucleus.
Ribosomes are the sites for protein synthesis.
Peroxisomes break down fatty acids to be used for forming membranes and as fuel for respiration. They also transfer hydrogen from compounds to oxygen to create hydrogen peroxide and then convert hydrogen peroxide into water.
Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They digest excess or worn out cell parts, food, and engulfed viruses or bacteria.