Session 8: The Reticular Formation - Control of Consciousness Flashcards
(38 cards)
Define arousal.
The emotional state associated with some kind of goal or avoidance of something noxious.
Define consciousness.
Something to do with awareness of both external world and internal states.
What two basic ingredients are required for consciousness?
The cerebral cortex and the reticular formation.
Explain the communication between the cerebral cortex and the reticular formation.
It is a positive feedback loop where the cortex excites the reticular formation and the reticular formation excites the cortex.

What is the reticular formation?
A population of specialised interneurones in the brainstem.
Input to the reticular formation.
Sensory system
Cortex
Outputs from the reticular formation.
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Basal forebrain nuclei
Spinal cord
Explain the basal forebrain nuclei pathway.
Information goes from the reticular formation in the lateral brainstem up to the basal forebrain nuclei.
Another neuron then goes to the cortex and synapse. It then uses ACh as an excitatory neurotransmitter.
Explain the hypothalamic pathway.
RF -> hypothalamus
Then to cortex and release histamine leading to excitation.
Explain the thalamic pathway.
RF -> Thalamus
Thalamus -> Cortex and releases glutamate leading to excitation.
What is a side effect of anticholinergics and antihistamines?
Drowsiness as they can inhibit the excitation of the cortex.

How do you assess consciousness?
Glasgow coma scale.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
What is assessed in GCS?
Eye opening
Motor response
Verbal response
What is the highest and lowest score on GCS?
15-3
Levels of eye opening.
4 - Spontaneous (full cortical)
3 - Response to speech (impaired cortical)
2 - Response to pain (no cortical)
1 - No response (brainstem dysfunction)
Levels of motor response
6 - Obeys command (full cortical)
5 - Localises motor response (cortical damage)
4 - Withdraw from the pain ellicited (only brainstem working)
3 - Flexor response to pain (decorticate lesion (above red nucleus))
2 - Extension response to pain (illogical) (decerebrate lesion (below red nucleus))
1 - No response
Levels of verbal response
5 - Oriented (What year is this - followed by correct answer)
4 - Confused conversation (will give wrong year but understood question) Cortical damage
3 - Inappropriate words (‘‘yesterday’’, ‘‘mother’’) Severe cortical damage
2 - Incomprehensible sounds like groans or screaming. Mediated by brainstem centers - subcortically
1 - No response
What does an EEG do?
Measures the combined activity of thousands of neurones in a given part of the cortex to a very high temporal resolution but very poor spatial resolution.
If the neurones gets deprived of sensory input (external stimulus), what will happen to the pattern of the firing of neurones.
They will start to fire in sync.
Give an example when neurones fire in sync.
During sleep
How many cycles of sleep does a person typically pass through in a night?
6
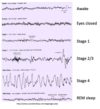
Stages of sleep.
Awake
Eyes closed
Stage 1
Stage 2/3
Stage 4
REM sleep
Going down the stages of sleep, how does the EEG pattern change?
A decrease in frequency and an increase in amplitude as the neurones starts to synchronise.
What stop the neurones from going into synchrony?
External stimulus


