Signs and symptoms Flashcards
(22 cards)
Skin maceration
Softening and breaking down of skin resulting from prolonged exposure to moisture
Sentinel pile
External lumps/skin tags associated with hemmorhoids or anal fissures
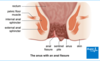
Where and what is McBurney’s point?
- the point corresponds to the most common location of the base of the appendix where it is attached to the cecum
- one-third of the distance from the anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus
Leucocytosis
Increased WCC
Guarding
Tensing muscles when pressure is applied to the area of concern
Purulent peritonitis
Presence of pus in the abdominal cavity
Feculent peritonitis
Intestinal perforation allowing feces into abdominal cavity
Glossitis
Inflammation with depapillation of the tongue, can be also sore; resulting in a smooth and erythematous surface; usually as a consequence of nutritional deficiencies
Aphthous ulcers
Bening and non-contagious mouth ulcers
Angular stomatitis
Inflammation of the corners of the mouth
Skin red, crusting, painful, itchy
Caused by infection, irritation and allergies
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
an autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by the development of benign hamartomatous polyps in the gastrointestinal tract and hyperpigmented macules on the lips and oral mucosa (melanosis)
Virchow’s node
Supraclavicular lymph node on the left side - gastric cancer
Koilonychia
Spoon nails, abnormally thin, flat to concave in shape - can be a sign of hypochromic anaemia especially iron deficiency anaemia
Pyoderma gangrenosum
a rare, inflammatory skin disease where painful pustules or nodules become ulcers that progressively grow

Haematemesis
Vomiting of fresh or altered blood
Malllory-Weiss syndrome/tear
Longitudinal tear or laceration of the mucous membrane, most commonly at the point where the oesophagus and the stomach meet (gastroesophageal junction). Such a tear may result in severe bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract; risk factors include alcohol use and hiatal hernia.
Odynophagia
Painful swallowing
Dysphagia
Difficulty in swallowing characterised as a sensation of obstruction during the passage of liquid or solid
Porphyria
a group of diseases in which substances called porphyrins build up, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system
Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person’s parents, and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme.
Myxedema
A collection of fluid in various tissues caused by deposition of glycosaminoglycans/mucopolysaccharides.
Aetiology - hypothyroidism and Grave’s disease
Examples: exophthalmos in Grave’s dis - collection behind the eye, pretibial myxedema, myxedematous heart disease - within the heart
Myopathy
Dysfunction of muscle without involvement of the neuromuscular junction or nerve supply
Symptoms - weakness, muscle pain, cramping, tetany


