Skin Disorders & Wounds Flashcards
(41 cards)
The _________ layer of the skin is thin and devoid of blood vessels and divided into outer hrny layer and inner cellular layer. It depends on the _______layer for nutrition.
Epidermis ; Dermis
The _______ layer is supplied with blood, contains connective tissue, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and hair follicles.
Dermis
The _________ contains adipose (fat tissue).
Subcutaneous tissues / hypodermis
Functions of the skin (4)
- ) Homeostasis - maintain pH
- ) Provides boundaries, protects underlying tissues from microorganisms, and radiation
- ) Modulates body temp
- ) Synthesizes vitamin D
_______ is the brownish pigment of the skin, genetically determined, increased by sunlight
Melanin
_______ is a golden yellow pigment that exists in subcutaneous fat and in heavily keratinized areas like palms and soles
Carotene
__________ is a bright red pigment, predominates in arteries and capillaries.
Oxyhemoglobin
_______ is darker somewhat bluer pigment from oxyhemoglobin losing its oxygen to the tissues. Increase in this pigment causes _________.
Deoxyhemoglobin ; cyanosis
_______ hair is short, fine, inconspicuous, and relatively unpigmented.
Vellus
________ hair is coarser, thicker, more conspicuous and usually pigmented (ex: scalp hair and eyebrows)
Terminal
Know the locations of:
lunula (whitish moon)
proximal nail fold
cuticle
lateral nail fold.

T/F
Nail plate gets pink in color from underlying vasular nail bed
True
T/F
Fingernails grow 0.1 cm/day
False
They grown 0.1mm/day
(and toenails grow slower than this)
______ glands produce a fatty substance that’s secreted onto the skin surface through the hair follicles
Sebaceous glands
_______ glands are present on all skin surfaces except palms and soles.
Sebaceous glands
There are two types of sweat glands.
_______ glands are widely distributed and open directly onto the skin surface, and help control body temperature.
_______ glands are found chiefly in axillary and genital regions, open onto hair follicles, and stimulated by emotional stress.
Eccrine glands ; Apocrine glands
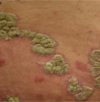
ABCDE screening moles for Melanoma
- *A** for Asymmetry
- *B** for irregular Borders, especially ragged, notched, or blurred
- *C** for variation or change in Color, especially blue or black
- *D** for Diameter > or equal to 6 mm or different from others, especially if changing, itching, or bleeding
- *E** for Elevation or Enlargement
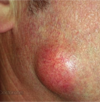
When assessing color for during a skin exam, what do you look for?
- increased pigmentation or loss of pigmentation
- redness & pallor (fingernails/ mucous membranes)
- cyanosis (central (trunk) & peripheral (fingers/toes))
- jaundice
What do you look for when assessing moisture when doing the skin exam?
dryness, sweating, and oiliness
How do you assess temperature when doing the skin exam?
use the backs of fingers to assess skin and any red areas for warmth
How do you assess mobility and turgor when doing the skin exam?
Lift skin and not ease with which it lifts up (mobility) and speed with which is returns into place (turgor - hydration status)
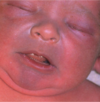
_______ is a slightly but uniformly pigmented macule or patch with a somewhat irregular border. It is flat and usually 0.5 - 1.5 cm in diameter.
Café-Au-Lait Spot
Six or more Cafe-Au-Lait spots each with a diameter > 1.5 cm suggests __________
Neurofibromatosis
___________ is depigmented macules (flat) appear on the face, hands, feet, and extensor surfaces (ex: back of elbow or neck), may be herediatary.
Vitiligo
* note * Brown pigment is normal skin, while the pale areas are vitiligo