Skull Flashcards
(89 cards)
Bregma of skull
at the junction of sagittal and frontal suture

Glabella of Skull
medium elevation between eye brows (supraciliary arches)

nasion of skull
at the junction of internasal and frontonasal sutures

pterion
a circular area formed by the junction of
- frontal bone
- sphenoid bone
- parietal and squamous part of temporal bone

What bones form the pterion?
- frontal bone
- sphenoid bone
- parietal and squamous part of temporal bone
What does the pterion mark?
marks the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery
lambda
at the junction of the lambdoid and sagittal sutures

What are the eight paired bones of the skull?
a. parietal - top of the skull
b. temporal - below parietal on the side of the skull
c. zygomatic - cheek bone
d. nasal - forming bridge of the nose
e. lacrimal - on the medial wall of the orbit
f. inferior concha - lower part of nasal cavity
g. palatine - posterior part of hard palate
h. maxilla - forming upper jaw
What are the six unpaired bones of the skull?
a. frontal - forehead
b. ethmoid - forming medial wall of the orbit and lateral wall of the nasal cavity
c. occipital - posterior aspect of skull - surrounds foramen magnum
d. sphenoid - a bat shaped bone, in most part located deep in the skull
e. vomer - forming inferior posterior part of nasal septum
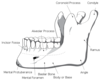
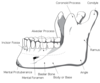
f. mandible - lower jaw
What paired bones enclose the cranial cavity?
a. parietal - top of head
b. temporal - side of head
What unpaired bones enclose the cranial cavity?
a. frontal - forehead region
b. occipital - back of head
c. sphenoid - base of cranial cavity
d. ethmoid - related to nose
What are the paired bones of the face?
a. zygomatic - cheek bones
b. maxilla - upper jaw
c. nasal - nose
d. lacrimal - in orbit
e. palatine - roof of mouth
f. inferior concha - in nose
What are the unpaired bones of the face?
a. vomer - nasal septum
b. mandible - lower jaw
What is endochondral bone formation?
has a cartilaginous model before bone is
formed
what is intramembraneous bone formation?
NO cartilaginous model
a. bone is formed directly from mesenchyme
What type of joints join the bones of the skull?
fibrous type of
joints - synchondroses
What are the three large important sutures of the skull?
a. sagittal suture - between parietal bones
b. coronal suture - between frontal and parietal bones
c. lambdoid suture - separates occipital bone from parietal and temporal
bones
What important formina can be seen from the superior aspect of the skull, and what passes through here?
parietal - for emissary veins

What bones can be see in the posterior region of the skull?
- squamous/flat part of occipital bone
- parietal
- mastoid process of the temporal bone
What sutures can be seen from the posterior aspect of the skull?
- lambdoid
- parietomastoid
- occipitomastoid
What is the median occipital crest?
it descends from external occipital
protuberance to the foramen magnum
a. provides attachment to ligamentum nuchae
What bones can be seen from the lateral aspect of the skull?
- frontal
- parietal
- temporal
- temporalis process of zygomatic bone
- sphenoid bone
- occipital bone
- mandible
- maxilla
What parts of the temporal bone can be seen when viewing the skull laterally?
a. squamous part - zygomatic process
b. tympanic part - external auditory meatus
c. mastoid process
What part of the spenoid bone can be seen when viewing laterally?
a. greater wing (probably lateral plate as well)