Spine Flashcards
(38 cards)
Spinal History Red Flags
(3)
- Fracture
- Trauma - remember, elderly may fx c minor tx
- Compression
- Tumor/Infection
- Hx cancer
- Constitutional changes
- > 50 yo
- Neuro compromise
- Cauda Equina Syndrome
- Ask about bowel/bladder function
- **Prepare to eval rectal tone **
- Cauda Equina Syndrome
Spine-Specific Hx Questions
(5)
- Injury
- Injury type
- Mechanisms
- violence
- work related
- Pain eval (OPQRSTUVW)
- ADL’s *(think bathing) *
- Bladder/bowl function
- Attempted tx
- OTC meds
- Massage
- Chiropractory
Spine Palpation
(4 aspects)
Check all points for pn/spasm while pt is standing (if possible)
- Spinous processes
- Paraspinal muscles
- Pelvis level
- SI joint
Neurological Components, Spinal Exam
(4 general)
Conduct on upper and lower limbs
- Dermatomes
- Reflexes
- Pulse
- Sensation
Gait Protocol
- Observe gait pattern when pt walks into room
- Antalgic (limping)
- Trandelenburg
- Short leg
- Foot Drop
- Have pt toe walk (S1)
- **Heel walk (L4/5) **
Standing Evaluation
- Nerve Root Tension - pt stand c one knee bent in spite of equal leg lengths (this poisition relieves tension)
- Prolapsed Intervertebral Disc - “List” or “tilt” may be compensatory for nerve root compression
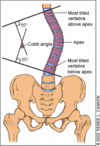
Abnml Spinal Curvature
- Spinally mediated (exaggerated curves)
- Muscle weaknesses/spasm

Spinal Landmarks
(
- T3 - spine of scapula
- T7 - just distal to inf angle of scapula
- L4 - Sacrospinalis
- S2 - Gluteus medius
These are helpful for palpating spinal tenderness - you can identify potential level of injury

Palpation Points, Spine
(5)
- Vertebral tenderness - localized vs generalized
- Paraspinal muscles - spasm/tenderness
- Sacroiliac joint - tenderness
- Groin - masses/abscesses
- Abdomen - masses/abscesses
Spinal ROM
- Flexion/extension
- Lateral flexion/extension
- Rotation L/R
Seated Inspection, Spinal Exam
(2 aspects)
- Observe movement on/off table
- Assess pt posture for obvious conditions
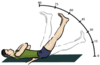
Straight Leg Raise (SLR)
- Lay pt supine
- Passively raise 1 leg at a time up to 60 degrees (going further may introduce hamstring tightness)
- Note the angle @ which pn radiating down leg occurs
+ exam = sciatic pn/parasthesia/discomfort/burning c ligament laxity that may be contra or ipsilateral to SC injury
- exam = 80-90 degrees s pn (potential tightness)
Sciatic Stretch Test
- Perform straight leg raise (passively flex leg from supine)
- Dorsiflex ankle
+ exam = additional nerve pn radiating down leg
Patrick’s/Faber’s Test
Procedure:
- Place pt supine
- Have pt place L knee just proximal to R patella
- Stabalize pelvis sharply, externally rotating hip to approach knee to table
- Repeat on other side
Results:
+ exam = hip/sacroiliac disease or injury
- exam = normal joint mobility
Spinally Relevant Reflexes
(7)
*Perform for upper and lower extremities, respectively *
- Biceps = C5
- Brachioradialis = C6
- Tricep = C7
- Knee = L4
- Ankle = S1
- Anal = S2/S3/S4 reflex arc (like cauda equina syndrome)
- Babinski = upper motor neurons
LE Myotomes
- Psoas = L2
- Quadriceps = L3 (L2/L3 disk)
- Tibialis Anterior = L4 (L3/L4 disk)
- Extensor Hallicus = L5 (L4/L5)
- Gastrocnemius, peroneus longus/brevis = S1 (L5/S1)
- Bladder sphincter = S2
- Anal sphincter = S3
*Remember, move these against resistance to test each motor neuron *
Lower Extremity Dermatomes
Only pay attention to left 2 pictures

LE Nerve Dependent Eval
(motor/reflex/sensation for L4/L5/S1)
-
L4
- Motor = tibialis anterior (inversion)
- Reflex = patellar
- Sensation = medial leg
-
L5
- Motor = extensor hallicus (toe dorsiflexion)
- Reflex = none
- Sensation = dorsum of foot
-
S1
- Motor = peroneus longus/breviw (eversion)
- Reflex = achilles
- Sensation = lateral foot

Upper Motor Neuron Dysfunction Signs
(3 exams)
- Hoffman’s Reflex
- pt seated c hand relaxed and cradled in yours
- flick middle finger nail
- watch for index finger/thumb flexion
- Babinski Reflex
- pt supine
- stroke lightly upward on plantar foot surface
- watch great toe extension
- Ankle clonus
- pt seated
- dorsiflex ankle suddenly
- observe rhythmic beating c duration and # of “beats”

S1 Tests
(3)
- Toe walking
- Straight leg raise
- Ankle reflex test
L4/L5 Specific Testing
- Lumbar list - *observe trunchal shift (L or R) when pt stands c feet together *
- Heel walking - L4
- Great toe extensor weakness - L5
Flip Test
(procedure, + result)
Procedure
- Sit pt on edge of table
- Passively flex pt hip (c knee straightened)
Positive - pt extends or “flips” backwards, indicating sciatic tension

Superficial Abdominal Index
(Procedure, Results, Indication)
Indication: perform to eval for paralysis in trauma pt
Procedure:
- pt supine
- stroke lightly towards umbilicus
Results:
- exam = pull umbilicus towards stimulated side
+ exam = no umbilicus movement
Piriformis Syndrome
Inflammation/pressure on piriformis muscle that compresses sciatic nerve and causes irritation
Often seen c wallet in back pocket