SS - Periodicity, crystal systems and unit cells Flashcards
(31 cards)
Define a lattice
An infinite array of points where each point has identical surroundings
Define a unit cell
A building block which when repeated in all directions gives the lattice
Define a lattice point
A single point within a lattice. The separation between lattice points is a, and knowledge of one point and a can build the whole lattice
Define a motif
Otherwise known as a basis. A motif/basis represents one or more atoms, ie a molecule or a protein. When a motif is placed on a lattice, a crystal structure is formed
Describe how to count atoms in a 2D representation
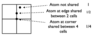
Describe how to count atoms in a 3D representation
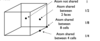
State the 4 types of unit cells
- Primitive (P)
- Body centred (l)
- Face centred (F)
- C centred (C)
Draw a primitive unit cell
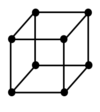
Draw a body centred unit cell
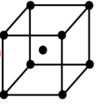
Draw a face centred unit cell
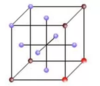
Draw a C centred unit cell

How many lattice points does a primitive unit cell have
1
How many lattice points does a body centred unit cell have
2
How many lattice points does a face centred unit cell have
4
How many lattice points does a C centred unit cell have
2
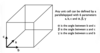
Draw a unit cell and label the parameters
Define bravais lattices
Combinations of the 7 unit cell shapes and 4 possible lattices give 14 Bravais laticces
State the 7 unit cell shapes
- Cubic
- Orthorhombic
- Tetragonal
- Triclinic
- Rhombohedral
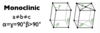
- Monoclinic
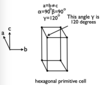
- Hexagonal
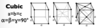
Give the parameters for a cubic unit cell
Give the parameters for an orthorhombic unit cell
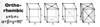
Give the parameters for a tetragonal unit cell
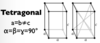
Give the parameters for a triclinic unit cell

Give the parameters for a rhombohedral unit cell

Give the parameters for a monoclinic unit cell