Structional Organization Flashcards
(64 cards)
Cells

Smallest and most numerous structural unit of living matter

Tissues
Comprised of groups of similar cells that perform specialized or common functions
Organs
Made up of tissues arranged together to perform a particular function
Systems
The organization of various organs so they can perform the many functions of the body as a whole
Cell membrane
Outer, semipermeable barrier that allows certain substances to pass through while blocking others
Nucleus
Sphere-like organelle within the cell, surrounded by a bilayer membrane that protects the structures within: nucleolus, nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and ribosomes
Chromosomes
Thread-like structures in the nucleus that control growth, repair, function, and reproduction
Cytoplasm
–Contains structures that consume and transform energy and perform the cell’s functions –Structures include: mitochondria (cell respiration and energy), lysosomes (degrade enzymes), ribosomes (synthesis proteins), golgi complex (secretion and intracellular transport), smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum (involved in protein and lipid synthesis)
Cyto
combining form for cell
-cyte
suffix for cell; smallest structural units of all living things
cytology
study of cells
cytologist
one who studies cells
cytometer
instrument used to count cells
cytometry
process of counting cells
cytotechnologist
technician who prepares slides
hist/o
Combining form for tissue
histology
study of tissues
histologist
one who studies tissues
histoblast
embryonic tissue cell
histoid
resembling tissue
Epithelial tissue
–Covers the internal and external organs of the body
–Lines the vessels, body cavities, glands, and body organs
Where is Epithelial Tissue Found
- Found in glands, ducts, and portions of the kidney tubules
- Found in the lining of the intestine and gallbladder
- Form the lining of cavities such as the mouth, blood vessels, and lungs
- Make up the skin surface and lining of the mouth, through the esophagus

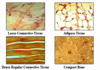
Connective Tissue
- –Supports and binds other body tissue and parts
- –Connective tissue consists of:
- liquid (blood)
- fats (lipids)
- fibrous (tendons and ligaments)
- cartilage (flexible elastic tissue)
- Solid (bone)
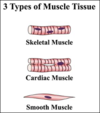
Three types of muscle tissue combing forms
- Skeletal muscle = rhabd/o/myo
- Smooth muscle = lei/o/myo
- Cardiac muscle = cardi/o/myo