Surgical Approaches Flashcards
(21 cards)
When using a lateral approach to the femur, especially when working proximally in the fem neck, why is it important to internally rotate the hip?
Rotating about 15 degrees overcomes the natural anteversion of the femur and brings it to a true lateral position
What structures are at risk during lateral approach to the femur?
Perforating vessels from the profunda femoris artery. Must be ligated to prevent a lot of bleeding.

What are the landmarks for incision to the medial parapatellar approach?
Straight midline about 5cm above sup pole of patella down to just below tibial tubercle

What is the internervous plane for the medial parapatellar approach?
None. If extended proximal, the plane is vastus medialis and rectus fem which are both fem n. innervation
In the medial parapatellar approach, should the patella be dislocated and everted when the knee is flexed or extended?
Should be done with the knee extended and then knee can be flexed afterword
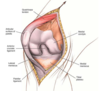
In med parapatellar approach, if having difficulty dislocating and everting patella, what can you do?
First try to extend incision proximally and further dissect quad muscles between vastus med and rectus. If that still doesn’t work you can remove part of patellar tendon with a bone block

What structures are at risk during med parapatellar approach?
Infrapatellar branch of saphenous nerve. If damaged, resect and bury in fat to prevent neuroma

Plates applied to the posteromedial tibia can help prevent what common deformity after proximal tibia fx?
Prevent varus deformity
Which side is the compression side of the tibia?
Medial
When doing the posteromedial approach to tibia and working on fxs there, which side should surgeon stand?
Contralateral side
Where is the incision made for the posteromedial approach to prox tibia?
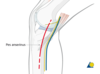
Directly overlying the posteromedial border of prox tibia. Length depends on pathology and implant. Or With the knee in slight flexion make a straight or slightly curved incision running from the medial epicondyle towards the postero-medial edge of the tibia. The incision can be extended as needed both proximally and distally as indicated by the dashed line.

What is the internervous plane for the posteromedial approach to the prox tibia?
There is not one. It is between the bone and the gastroc.
What structures are at risk during posteromedial approach to prox tibia?

Saphenous vein and nerve are post to incision and must be protected. The Pes Anserine tendons and mcl are also at risk.
When measuring compartments with a stryker needle, where should the needle be placed in relation to the fracture site?
Within 5cm of fracture site
Where is the stryker needle entry point for measuring ant compartment of leg?
1cm lateral to ant tibia, within 5cm of fx
Where is the entry point for measuring deep post compartment of leg pressures?
Just post to med border of tibia

Where is entry point for measuring compartment pressures in lateral and sup post compartment of leg?
Lateral is just ant to post border of fibula w/in 5cm of fx. Superficial post is middle of calf w/in 5cm of fx if possible.

How does measuring compartment pressures in a hemophiliac differ from other pts?
You should give them factor VIII before measuring
What are the 2 main ways you can release compartments in the lower leg?
Dual medial-lateral incision or a single lateral incision
How is the dual medial-lateral incision performed for compartment release?
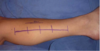
- Incisions should have a 8cm skin bridge between. Both incisions start at tibial tubercle and stop 6cm above ankle joint. 15-18cm incisions
- Lateral: protect sup peroneal n. Ant comp fascial incision 1cm ant to intermuscular septum and lateral comp 1cm post to septum
- Medial incision: Protect saph n and vein. Incise sup post fascia. You MUST detach soleal bridge from back of tibia for complete release.



