Symbol/picture cards Flashcards
(21 cards)
Give the formula for determining the fraction of total receptors bound with a ligand

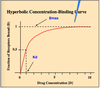
Recall the hyperbolic concentraiton binding curve of a drug, where would its Kd fall?
Recall a sigmoidal receptor binding curve expressed with and without sem-log transformation.

Define:
Emax
ED50
Emax: The maximum response achieved by an agonist (drug efficacy)
ED50: The drug dose at which 50% of Emax is achieved (potency)

Recall a quantal dose-response curve
- Useful to describe population rather than single individual response to drugs
- Based on plotting cumulative frequency distribution of responders against the log drug dose (may sometimes have a drug that can’t affect 100% of people)

Recall the impact of inverse agonist, atagonist and agonist on blood vessel diameter and constitutive receptor activity
How is the therapeutic index of a drug determined?
Whether or not something has good therapeutic index depends on what the toxic effect is (eg. headaches vs. death)
In general, a larger TI indicates a clinically safer drug

Give the formula for determining volume of distribution (Vd) immediately after bolus injection
Q: Total amount of drug in body (dose)
Co: initial plasma concentration
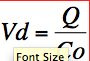
Give the equation for IV bolus pharacokinetics (elimination) with the single compartment model

Give the equation for single compartment IV bolus eliminiation half life (T1/2)

Recall the half life graph for a single compartment IV bolus injection.

Give the formula for clearance with kel

Give the formula for drug half life with clearance (Cl)
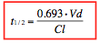
A drug has a minimum therapeutic concentration of 2 μg(mL-1), what dose should Joe receive to achieve teh minimum therapeutic plasma concentration if it has a volume of distribution (Vd) of 20 L?
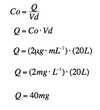
Recall a schematic for two methods of maintaining steady state (Css) without IV
- Repeated dosages
- First large dose (loading phase) then maintenance

Why is compliance of drug dosage scheduling so important?
Changing dosing intervals can lead to no effect, or toxic effect.

Recall the four most important pharmacokinetic equations

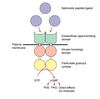
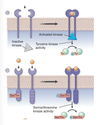
Recall the two common transmembrane receptors with intrinsic enzyme activity.
Tyrosine Kinases-containing Receptors - Receptors that have intrinsic catalytic activity (tend to dimerize)
e.g. for growth factors such as epidermal growth factor (EGF).
Tyrosine Phosphatase receptors – Receptors that dephosphorylate tyrosine residues on proteins (don’t tend to dimerize)

Recall the two common transmembrane receptors that link to an enzyme activity
Tyrosine Kinase-linked Receptors - Receptors that work through associated proteins
e.g. for cytokines that control the immune response such as the interleukins (ILs).
Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinase e.g TGFβ receptor. More involved in longer term response than G proteins.
Recall the guanylyl cyclase receptor
Stimulation modulates: phosphodiesterase (breaks down GTP), PKG and ion channels