Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones Flashcards
(73 cards)
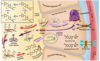
Describe the step 2 of the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones
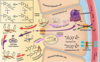
Oxidation of iodide to to iodine by thyroid peroxidase (TPO) in the peroxisome
Triiodothyronine is conjugated, also on the outer ring, with sulfate in a reaction catalyzed by:
Phenol Sulfotransferase
Mention the function of T3 on the heart
Increase:
- Heart Rate
- Hypertrophy
Describe the feedback effect
Entire cycle that delicately balanced to maintain stable levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) in the blood, involving TRH, the pituitary and hypothalamus.
_____________ condition in which the thyroid gland produces and secretes excessive amounts of thyroid hormones: T3 and/or thyroxin T4.
Hyperthyroidism
Accounts for 80%95% of thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid gland
T4
In children, hypothyroidism leads to delays in growth and intellectual development, which is called _________
Cretinism
Wich transport mechanism is associated with Iodine?
Sodium Iodide (Na+ I−) symporter (NIS)
In human beings and monkeys, circulating T4 is bound primarily to:
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)
The α-subunit has an identical structure to other hormones (LH,FSH, hCG) but the β-subunit is specific.
TSH
What type of reaction occur in the liver, kydeys or elsewhere that is important to metabolism?

- Monodeiodination of Thyroxine (deiodination of T4)
- The removal of an iodine molecule from the 5’ position on the outer phenolic ring by 5-deiodinase results in T3
Mention the function of T3 on the Bone
Increase:
- Growth and maturation
- Resorption
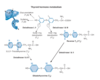
__________is bound to tyrosyl residues in thyroglobulin to form, successively, _____________ and ____________ .
- Iodine
- Monoiodotyrosine (MIT)
- Diiodotyrosine (DIT)
________ acts on the pituitary gland to trigger more TSH release
TRH
The number of TRH receptors on the thyrotropes is regulated by:
The concentration of both TRH itself and of the thyroid hormones
Describe the Step 4 of the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones

Coupling of iodinated tyrosine residues to form either T4 (DIT+DIT) or T3 (MIT+DIT).
Conjugated thyroid hormones (with sulfate and glucuronic acid) are excreted in the bile, passing into the intestine, where some of the iodine is reabsorbed by ______________
Enterohepatic Circulation
Increase in intracellular___________ leads to the release of intracellular __________, which in turn results in secretion of ___________.
Inositol triphosphate (IP3 )
Calcium
TSH
Mention the function of T3 in the liver
Increase:
- Cholesterol synthesis
- Cholesterol absorption from plasma
- Conversion of cholesterol to bile acids
- Fat Oxidation/Synthesis Glucogenesis
Describe the Step 6 of the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones

The thyroid hormones are transported to the plasma membrane and released into the bloodstream
Mention the autoimmune condition that consist in attack of the immune system to the thyroid gland, specially the follicle cells, and is the most common cause of hypothyroidism
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
______________ are degraded primarily by conjugation in the liver
Thyroid Hormones
If the ______________ are low, then the ___________ will secrete more TSH and if ______________ levels in the blood are too high, then pituitary gland secretes less ____________.
- Thyroid hormones
- Pituitary gland
- T3 and T4
- TSH
__________ is formed in peripheral tissues by deiodination of T4.
T3