Term 1 Year 11 Flashcards
to learn lul (54 cards)
Which are the four factors of production?
It is: Land, Labour, capital and enterprise.
What is Relative Scarcity
Relative scarcity means that we do not have enough resources to satisfy all our wants and needs.
What is consumer Sovereignty
It is the situation in an economy where the desires and needs of consumers control the output of producers.
What is consumer elasticity
Consumer elasticity is the amount of patience a consumer has for change in prices before they stop purchasing the product. If a consumer is elastic
What is opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is the opportunity that is wasted when purchasing an item. An example of this would the opportunity cost of buying a coke would be the materials used to make the coke could have made something else for the people that need it most.
What are the rewards for factors of production
Land —–> Rent Labour –> Wages Capital –> Intrest Enterprise –> Profit
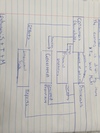
What does the Circular Flow Of Income Look Like?
What is Producer Sovereignty
Factors that can reduce the effects of consumer sovereignty. An example of this is marketing and misleading conduct.
What does Y, C, S stand for and how do we find the Y
Y= Disposable income after tax
C = Consumption
S= Savings
You can find Y but adding C and S
How to find the Average propensity to Consume
APC = C/Y
How to find the Average Propensity To Save
APS = S/Y
How to find Marginal Propensity to Consume
MPC = Change of C
Change of Y
How to find the Marginal Propensity To Save
MPS = Change Of S
Change Of Y
What does the Life Cycle Theory Of Consumption Look Like

What does Economies of Scale Graph Look Like

What are Internal Economies Of Scale
Internal economies of scale refer to a reduction in the average cost of production as output increases because of more efficient use of the firm’s resources. This can be due to many things that operate inside the firm.
What are external economies of scale
External economies of scale result from reductions in average costs as output increases due to factors outside the firm’s direct control. This could be things like growth in the industry where the firm operates and Localisation.
What are Diseconomies of Scale
Diseconomies of scale are disadvantages associated with a firm growing too large. This occurs beyond the ‘technical optimum’ level of output.
What are internal diseconomies of scale
Internal diseconomies of scale refers to an increase in the average cost of production as output increases. Internal diseconomies of scale may result from bottlenecks in production such as equipment failure and more.
What are external Diseconomies of scale
External diseconomies of scale refer to an increase in the average cost of production as output increases. This is influenced by something that the business can’t control. Such as loss of growth in the industry which the firm operates and also bad localization
What is the law of demand
The higher the price of a good/service, the quantity of demand for that product will fall. Factors affecting market demand:
*The price of the good itself
*The price of another good or service
*Expected future prices
*Change in consumer taste/preferences
*The level of income
*Size of population and age distribution
What are some factors that cause an increase in demand.
factors include: *Prices of other competing goods and services.
*A rise in substituting goods
*A fall in the price of complementary goods.
What is the demand schedule
The demand schedule shows the quantity of a good/service that is demanded over a range of prices in a given period of time. It is represented in a table.
What is the law of supply
The higher the price of a good/service, the quantity supplied by producers in that industry rises and vice-versa


