Test 5 - pulmonary Flashcards
(159 cards)
What are the clinical symptoms of brocnhitis? Is fever a common symptom?
productive cough
wheezing
fever is unusual
How is bronchitis diagnosed?
Clinical diagnosis - based on symptoms of cough, wheezing. CXR is only indicated if pneumonia is suspected, and if consolidation is not seen pneumonia can be ruled out.
What is pneumonia?
Infection of the lung parynchyma (respiratory airways)
Pneumonia is categorized into 4 types. Name these 4 types (one type is further divided into two categories)
Community acquired (typical and atypical)
Hospital acquired
Health-care associated
Opportunistic
What are the clinical symptoms of pneumonia?
fever
chest pain
dyspnea
productive cough
How is pneumonia diagnosed? Is culture often performed?
Diagnosis is made with clinical symptoms and a chest x-ray with focal lung opacities
Culture is not usually performed because patients cannot expectorate sputum and even if they can the culture is contaminated with oropharyngeal bacteria
How is pneumonia treated? discuss community-acquired and hospital-acquired treatments

What is Mycobacterium tuberculosis? (stain, shape, and type of microbe)
Tuberculosis is an acid fast rod bacterium
How is TB transmitted?
air droplets
Describe the potential course of TB (primary infection, etc)

What are the general clinical symptoms of TB?
productive cough
fever
malaise
weight loss
+/- hemoptysis
If TB becomes systemic, what diseases can the patient develop?
Pott’s disease (TB in the vertebrae)
Milliary disease (widespread dissemination)
How is active TB diagnosed (there are a few methods you should name)? Can IGRA or a PPD test diagnose active TB?
CXR
Sputum smear with acid fast stain (takes 4-6 weeks to culture)
nucleic acid amplification
IGRA and PPD CANNOT diagnose active TB

Is PPD specific to Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
If the patient recieved a BCG vaccination, PPD will yield a positive result
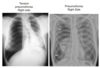
How does primary TB and secondary TB present on CXR?
Primary TB has cavitary lesions in the lower/middle lobe(s)
Secondary has cavitary lesions in the upper lobe(s)
Note: hilar LAD may be present in both

What are risk factors for developing active TB?
Malnutrition
immunocompromized patients (drugs, HIV)
Diabetes
alcoholism
children under 2 years of age
How is TB treated?

What type of infectious agent causes pneumocystis pneumonia and in what patient population is this infection seen in?
PCP is a fungal pneumonia (caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii) that is commonly seen in AIDS patients with a CD4 count below 200
What are the clinical symptoms of pneumocystis pneumonia?
fever
non-productive cough
dyspnea
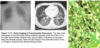
How is pneumocystis diagnosed?
Chest imaging (ground glass opacities) +/- “crushed ping-pong balls” opacities
Bronchoalveolar lavage crushed ping-pong balls morphology
What is the treatment for pneumocystis pneumonia?
Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim)
What is bronchiolitis?
Inflammation of the bronchioles
What age is bronchiolitis typically seen in? What are the clinical symptoms of bronchiolitis?
Seen in children under 6 months
coryza (stuffy nose)
Rhinorrhea (runny nose)
cough
wheezing
chest wall retractions
respiratory distress
difficulty feeding due to increased work of breathing
How is bronchiolitis diagnosed?
CXR:
air trapping
peribronchial thickening
subsegmental opacities