The hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal axis: posterior pituitary Flashcards
(45 cards)
Name the hormones produced by the posterior pituitary gland
Oxytocin and Vasopressin (ADH)
Name the artery located in the posterior pituitary gland
Inferior hypophysial artery add pic

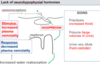
What is different about the nuerons coming from paraventricular nuclei and the supra-optic nuclei?
Some of the neurons which originate in the paraventricular nucleus terminate on the walls of the primary capillary plexus in the median eminence whilst the nuerons in the supra-optic nuclei only terminate in the posterior pituitary gland.
add pic
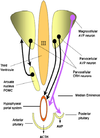
What are the majority of the nuerones that are located in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei and secrete ADH and Oxytocin?
Magnocellular nuerones add pic

Where are supraoptic nuerones located?
Supraoptic nuclei add pic

What are herring bodies?
Herring Bodies - areas where the neurosecretions can be stored on the way down to the neurohypophysis.
Molecules can be released from the herring bodies .
Where do supraoptic nuclie terminate?
Nuerohyophyis
Where do the supraoptic nerurones pass through?
The median eminence-They don’t terminate there add pic

What substances do supraoptic nuerones produce?
Oxytocin or vasopressin
Magnocellular nuerones in the supraoptic nuclie either express vasopressin or ocytocinergic
add pic

Where do paraventricular neurones originate from?
Paraventricular nuclei.
Name the other places the parvocellular nurones terminate at?
Some (parvocellular) neurones pass to other parts of brain.
Some (parvocellular) VP neurones terminate in median eminence
add pic

Name the type of nurones found in the paraventricular nuclie?
Magnocellular ( Pass to the neurohypophysis).
Parvocellular (terminate in the brain or the median eminnance)
Why do some parvocellular neurones pass to other parts of the brain?
Oxytocin and vasopressin effect behavior
Where do magnocellular neurones terminate at?
neurohypophysis
Vasopressin can be deposited in the nuerohypophysis and where else by the paraventricular nuerones?
Median eminance
These neurones also synthesize corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), which acts synergetically with vasopressin to stimulate release of adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) from the pituitary gland
The CRF and ADH is released at the same time.
State the difference between Vasopressin and Oxytocin in terms of their structure?
VP has Phenylalanine instead of Isoleucine.
VP has Arginine instead of Leucine. They differ by TWO AMINO ACIDS.
Because they have similar structures VP can have similar effects to oxytocin and vice versa. These effects however are not as strong.
add pic
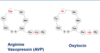
What does the vasopressin prohormone break down into?
Vasopressin (Arginine Vasopressin - AVP) .
Neurophysin (large protein which is specific to the provasopressin molecule).
Glycopeptide (may be a prolactin releasing factor but little is known about it) . add pic

List the steps for vasopressin synthesis.
Pre-Prohormone- the signal peptide is cleaved.
Then it is a prohormone.
Then it is cleaved again to make Vasopressin and Neurophysin and glycopeptide.
add pic

What is the difference between oxytocin synthesis and vasopressin synthesis?
Same sequence for oxytocin synthesis, except that the neurophysin differs slightly and the glycopeptide is absent
Pre-prooxytocin splits into TWO.
add pic

Name two nonapeptides
Oxytocin and vasopressin
What is nuerophysin function?
The nuerophysin binds to the oxytocin or the vasopressin and prevents oxytocin and vasopressin diffusing out of the herring body.
Nuerophysin also prevents enzyme degregation of the hormones.
What physiological actions on the body occurs when vasopressin binds to V1 receptors?
List what happens for V1a and V1b Receptors?
add pic

What physiological actions on the body occur when vasopressin binds to V2 receptors?
add pic

List the sequence of events within a cell when vasopressin binds to a V1 receptor
Linked via G proteins to phospholipase C.
Which acts on membrane phospholipids to produce inositol triphosphate IP3 (and diacyl glycerol, DAG) which increase cytoplasmic [Ca2+] and other intracellular mediators (PKC) which produce cellular response
add pic