Things Flashcards
(24 cards)
Mechanisms of injury from lightening
- Direct hit (usually fatal)
- Splash (from ground to person)
- Conduction Ground Current
Lightening Injury Management
- Reverse Triage (pulseless gets most attention)
- Monitor for:
- ventricular dysrhythmias,
- rep depression, s
- seizure
Lightening Injuries
VT/VF, asystole, apnea, seizures Keranuparalysis – vasospastic paralysis of LE, resolves spontaneously Lichtenburg sign – arboreal pattern Cataracts
Liver Abscess
- Usually R lobe of liver, can be associated with R pleural effusion
- Pyogenic – caused by ascending infection from biliary tract (i.e. obstruction, cholangitis) and other belly infx (appy) (klebsiella, e coli)
- These need admission for IV abx, drainage (perc)
- Amebic – entamoeba histolytica, history of camping in midwest, can trial PO Flagyl x 7 days
Otitis Externa management
Mild - acetic acid/hydrocortisone
Moderate - ciproodex (not with perforation) (cipro alone OK)
Severe - ciprodex and wicks
MOE –> diabetics, chemo, immusupressed etc… -failure to respond to conservative tx
- -fever -elevated inflammatory markers, CT/MRI for osteomyelitis, CN involvement, trismus -needs ENT, maybe IV abx, sx.
Rectal Prolapse
- If prolonged can lead to edema, ischemia
- May need sedation for reduction
- Can use regular sugar to reduce edema before reduction
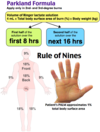
Parkland
Hydrocarbon Inhalation
Need at least 6hr obs
CXR with patchy infiltrates
Avoid catecholiminergic meds –> sensitizes myocardium and can lead to TdP VT VF etc…
Febrile Seizure –> complex vs simple
Simple = <15 minutes, non-focal, no more than 1 in 24h
Complex = anything not simple
If complex, need labs, +/- LP
Pediatric Hypoglycemia Treatment By Age
<2 mo –> D10w 5 mL/kg
2mo-8 years –> D25 2 mL/kg
>8 D50 1 mL/kg
D10W for maintenance
Push Dose Epi
9 mL NS + 1 mL of code dose epi (1:10,000)
There are 1000 mcg in 10 mL code dose epi (100 mcg/mL) so –>
push dose has 10 mcg/mL
Giving 1-2mL/min push dose = epi gtt at ~ 0.1-0.2 mcg/kg/min
1:1000 injection anaphylaxis = 1 mg/mL, while epinephrine 1:10,000 = 0.1 mg/mL.
Tooth Avulsion Management
Handle by CROWN only
Rinse in saline
Re-implant and splint
24-48h dental follow up
Liquid DIET
Guillane Barre W/u and Tx
Ascending weakness, symmetric, sensation preserved.
Can see autonomic dysfunction
CSF with increased protein, but normal WBC counts
Tx plasmapheresis and or IVIG
Check NIF!
Physiologic changes during pregnancy

Duration of calcium gluconate
30-60 minutes
Can redose after an hour
Classic ECG Finding in Tricyclin OD
Wide QRS AND terminal R wave in aVR

Sigmoid vs Cecal Volvulus
Sigmoid = coffee bean sign on XR, if not s/s perforation/ischemia can have sigmoidoscopy to decompress and sx is definitive managaement
Cecal volvulus ALWAYS needs sx.
Indications for Thoracotomy after Chest Tube

Other non biliary causes of RUQ pain
RLL PNA
PE
Fitz-Hugh Curtis
Think of in pleuritic RUQ pain.
Ethylene Glycol Characteristics
Nonspecific presentation initially – i.e. intoxication.
Later leads to cardiopulmonary, metabolic derangement (hypocalcemia), ARDS
Renal failure after 1-3 days with stones
HAGMA
Osm Gap from PARENT Alcohol, not metabolites
Fluoresces under Woods Lamp (though this is neither specific nor sensitive)
Rx Fomepizole (better tolerated than etoh)

Indications for HD in salisylate toxicity
AMS (cerebral edema)
Pulmonary Edema
Level > 100 mg/dL or rapidly rising level
Renal failure
Severe acid base d/o
Otherwise, rx = NaHCO3
Salicylate toxicity management
HD if severe
Bicarb –> ~2 amp IVP and then gtt
Give bicarb push prior to tube (but don’t tube)
Can given charcoal if close to ingestion
D50 regardless of glucose
IVF
Medications that can be removed with dialysis
- Salicylates
- Methanol
- Ethylene glycol
- Lithium
- Theophylline
- Carbamazepine
- Amanita mushrooms
Activated Charcoal Indications
- Overall, short time since ingestion (1-2), or drug delays gastric empyting, or is controlled release
-
Meds
- colchicine
- CCBs
- Cardiglycosides (DIG)
- Cyclis (TCAs)
- Salicylate


